A 44-Year-Old Alcohol-Dependent Man Who Recovered from Central Pontine Myelinolysis with Supportive Physical Therapy
- PMID: 36081331
- PMCID: PMC9472294
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.937389
A 44-Year-Old Alcohol-Dependent Man Who Recovered from Central Pontine Myelinolysis with Supportive Physical Therapy
Abstract
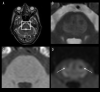
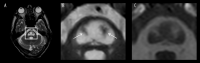
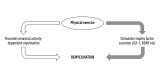
BACKGROUND Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) includes symmetric demyelination of the central pons. CPM is a rare neurological disorder that generally develops after rapid correction of hyponatremia in individuals having underlying conditions, such as malnutrition, alcoholism, and severe burns. It can cause severe long-term disabilities. However, there is currently no pharmacotherapy capable of promoting remyelination, a process crucial for recovery from CPM. We present the case of a patient with alcoholism and malnutrition-related CPM, which developed following rapid correction of hyponatremia but then improved remarkably with supportive physical therapy. CASE REPORT A 44-year-old alcoholic and malnourished man was admitted to an emergency hospital for disorientation due to overdrinking, but later developed bulbar palsy after hyponatremia was unexpectedly, but rapidly, corrected. Axial scans of the diffusion-weighted brain MRI revealed a characteristic lesion known as a piglet sign in the central pons. Based on his underlying conditions, present episode of sodium correction, and MRI finding, the patient was diagnosed as having CPM, which progressively worsened, resulting in locked-in syndrome after 12 days. The patient was then transferred to a long-term care unit and received simple motion exercise daily, but no specific medication. His symptoms gradually improved, achieving discontinuation of tube feeding on day 21, independent walking on day 110, and discharge after 6 months. CONCLUSIONS This report highlights the importance of physical therapy, the potential of which is often underestimated despite its broad benefits for human health, as a readily applicable intervention for patients with CPM. Further understanding of mechanisms underlying exercise-induced myelination should contribute to establishing novel therapies for a wide spectrum of brain disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Central Pontine Myelinolysis Due to Chronic Alcohol Use: Case Report.Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2020 Dec;29(4):119-123. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2020. PMID: 34018171
-
[Central pontine and extra-pontine myelinolysis in an alcoholic patient without hydro-electrolyte disturbances: case report].Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002 Dec;60(4):1030-3. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x2002000600028. Epub 2003 Jan 15. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002. PMID: 12563402 Portuguese.
-
Temporal evolution of the trident and piglet signs of osmotic demyelination syndrome.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Feb 15;373:268-273. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.01.024. Epub 2017 Jan 7. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28131203
-
Central pontine myelinolysis secondary to rapid correction of hyponatremia historical perspective with Doctor Robert Laureno.Neurol Sci. 2021 Aug;42(8):3479-3483. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05301-3. Epub 2021 May 5. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33950364 Review.
-
Central pontine myelinolysis.Eur Neurol. 2002;47(1):3-10. doi: 10.1159/000047939. Eur Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11803185 Review.
Cited by
-
Physical activity and the brain myelin content in humans.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jun 5;17:1198657. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1198657. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37342769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical Exercise Counteracts Aging-Associated White Matter Demyelination Causing Cognitive Decline.Aging Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(5):2136-2148. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0216. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38377028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singh TD, Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA. Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: A systematic review. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(12):1443–50. - PubMed
-
- Amann B, Schäfer M, Sterr A, et al. Central pontine myelinolysis in a patient with anorexia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 2001;30(4):462–66. - PubMed
-
- Cohen BJ, Jordan MH, Chapin SD, et al. Pontine myelinolysis after correction of hyponatremia during burn resuscitation. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1991;12(2):153–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

