Efficacy and safety of biological agents for the treatment of pediatric patients with psoriasis: A bayesian analysis of six high-quality randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36081503
- PMCID: PMC9446895
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.896550
Efficacy and safety of biological agents for the treatment of pediatric patients with psoriasis: A bayesian analysis of six high-quality randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Biological agents have been used with extreme caution in children because of their possible adverse effects.
Objectives: This study used high-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to provide high-level evidence to assess the effectiveness and safety of biological agents for treating children with psoriasis.
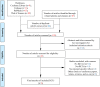
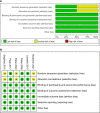
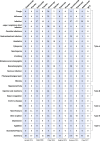
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and Web of Science databases through October 31, 2021. We included trials reporting at least one adverse event after treatment with biological agents of patients less than 18-year-old diagnosed with psoriasis. RevMan 5.3 and Stata 15.0 software were used for meta and Bayesian analyses.
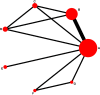
Results: Six trials with 864 participants were included in the analysis. The results showed a 2.37-fold higher response rate in all biologics groups than in the control group for psoriasis area and severity index 75 (PASI75) (RR= 2.37, P-value < 0.01, 95% confidence interval [CI] [1.22, 4.62]). Compared with placebo, the PASI75 response rates of etanercept (RR= 2.82, 95% [CI] [1.10, 7.21]), ustekinumab low dose (RR= 7.45, 95%[CI] [1.25, 44.58]), and ustekinumab high dose (RR= 7.25, 95%[CI] [1.21, 43.41]) were superior. Additionally, the incidence of total adverse reactions was 1.05 times higher for biologics than for controls, indicating a good safety profile (RR= 1.05, P-value = 0.53, 95%[CI] [0.92, 1.19]). Overall, these six high-quality randomized controlled trials suggest that biologics are effective and safe for pediatric patients with psoriasis.
Limitations: Inclusion of few relevant, high-quality RCTs.
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that biologics can be used to treat children with moderate-to-severe psoriasis without the risk of adverse effects. Ustekinumab showed the best efficacy and the fewest adverse effects.
Keywords: Bayesian analysis; adverse events; biological agents; pediatric; psoriasis; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Cai, Ru, Liu, Sun, Zhou, Luo, Chen, Zhang, Wang, Li and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
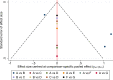
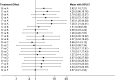
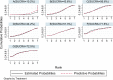
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

