Sirolimus combined with interferon-alpha 2b therapy for giant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a case report
- PMID: 36081563
- PMCID: PMC9447363
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.972306
Sirolimus combined with interferon-alpha 2b therapy for giant hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a case report
Abstract
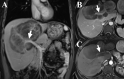
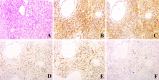
Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (HEH) is a very rare tumor originated from vascular endothelial cells, with unpredictable malignancy. No standard treatment has been established yet. Although surgical resection and liver transplantation have been reported to be effective treatments with favorable long-term outcomes, the multiple intrahepatic lesions or extrahepatic metastasis makes these procedures unsuitable to most patients. Sirolimus was reported to be an effective drug for epithelioid hemangioendothelioma but only about 10% achieved partial response. Interferon-alpha 2b (IFN-a 2b) has also been used for the treatment of HEH, and the rate of tumor regression was more than 50%. Here, we report a HEH patient with giant intrahepatic tumor (>15cm), who achieved partial response after the combined therapy of sirolimus and IFN-a 2b. The giant intrahepatic lesion (>15 cm) regressed obviously after 8 months treatment and no severe adverse event was reported. The good response and safety of combined therapy with sirolimus and IFN-a 2b provide a promising guidance for future clinical study.
Keywords: case report; epithelioid hemangioendothelioma; interferon; liver; sirolimus.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhou, Si, Liu, Yang, Han and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

