Peripheral fractional oxygen extraction measured with near-infrared spectroscopy in neonates-A systematic qualitative review
- PMID: 36081622
- PMCID: PMC9445360
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.940915
Peripheral fractional oxygen extraction measured with near-infrared spectroscopy in neonates-A systematic qualitative review
Abstract
Background: Peripheral fractional oxygen extraction (pFOE) measured with near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in combination with venous occlusion is of increasing interest in term and preterm neonates.
Objective: The aim was to perform a systematic qualitative review of literature on the clinical use of pFOE in term and preterm neonates and on the changes in pFOE values over time.
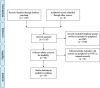
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase and Medline was performed using following terms: newborn, infant, neonate, preterm, term, near-infrared spectroscopy, NIRS, oximetry, spectroscopy, tissue, muscle, peripheral, arm, calf, pFOE, OE, oxygen extraction, fractional oxygen extraction, peripheral perfusion and peripheral oxygenation. Additional articles were identified by manual search of cited references. Only studies in human neonates were included.
Results: Nineteen studies were identified describing pFOE measured with NIRS in combination with venous occlusion. Nine studies described pFOE measured on the forearm and calf at different time points after birth, both in stable preterm and term neonates without medical/respiratory support or any pathological findings. Nine studies described pFOE measured at different time points in sick preterm and term neonates presenting with signs of infection/inflammation, anemia, arterial hypotension, patent ductus arteriosus, asphyxia or prenatal tobacco exposure. One study described pFOE both, in neonates with and without pathological findings.
Conclusion: This systematic review demonstrates that pFOE may provide additional insight into peripheral perfusion and oxygenation, as well as into disturbances of microcirculation caused by centralization in preterm and term neonates with different pathological findings.
Systematic review registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/], identifier [CRD42021249235].
Keywords: disturbances in microcirculation; microcirculation; near-infrared spectroscopy; pFOE; pOE; peripheral fractional oxygen extraction; peripheral muscle oxygenation.
Copyright © 2022 Wolfsberger, Hoeller, Suppan, Schwaberger, Urlesberger, Nakstad and Pichler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Wardle SP, Yoxall CW, Crawley E, Weindling AM. Peripheral oxygenation and anemia in preterm babies. Pediatr Res. (1998) 44:125–31. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical