Development and validation of a predictive model for new-onset atrial fibrillation in sepsis based on clinical risk factors
- PMID: 36082114
- PMCID: PMC9447992
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.968615
Development and validation of a predictive model for new-onset atrial fibrillation in sepsis based on clinical risk factors
Abstract
Objective: New-onset atrial fibrillation (NOAF) is a common complication and one of the primary causes of increased mortality in critically ill adults. Since early assessment of the risk of developing NOAF is difficult, it is critical to establish predictive tools to identify the risk of NOAF.
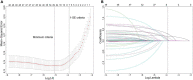
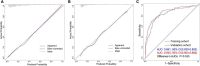
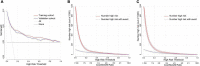
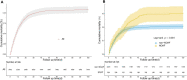
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled 1,568 septic patients treated at Wuhan Union Hospital (Wuhan, China) as a training cohort. For external validation of the model, 924 patients with sepsis were recruited as a validation cohort at the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Urumqi, China). Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to screen predictors. The area under the ROC curve (AUC), calibration curve, and decision curve were used to assess the value of the predictive model in NOAF.
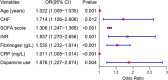
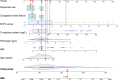
Results: A total of 2,492 patients with sepsis (1,592 (63.88%) male; mean [SD] age, 59.47 [16.42] years) were enrolled in this study. Age (OR: 1.022, 1.009-1.035), international normalized ratio (OR: 1.837, 1.270-2.656), fibrinogen (OR: 1.535, 1.232-1.914), C-reaction protein (OR: 1.011, 1.008-1.014), sequential organ failure assessment score (OR: 1.306, 1.247-1.368), congestive heart failure (OR: 1.714, 1.126-2.608), and dopamine use (OR: 1.876, 1.227-2.874) were used as risk variables to develop the nomogram model. The AUCs of the nomogram model were 0.861 (95% CI, 0.830-0.892) and 0.845 (95% CI, 0.804-0.886) in the internal and external validation, respectively. The clinical prediction model showed excellent calibration and higher net clinical benefit. Moreover, the predictive performance of the model correlated with the severity of sepsis, with higher predictive performance for patients in septic shock than for other patients.
Conclusion: The nomogram model can be used as a reliable and simple predictive tool for the early identification of NOAF in patients with sepsis, which will provide practical information for individualized treatment decisions.
Keywords: SOFA score; new-onset atrial fibrillation; nomogram; predictive model; sepsis.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Pang, Li, Yu, Peng, Hu, Niu, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myeloperoxidase and its derivative hypochlorous acid combined clinical indicators predict new-onset atrial fibrillation in sepsis: a case-control study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04034-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39030470 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a nomogram prediction model for the risk of new-onset atrial fibrillation following percutaneous coronary intervention in acute myocardial infarction patients.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Nov 13;24(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04326-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39538121 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for 3- and 5-year new-onset atrial fibrillation in HFpEF patients.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 16;11:1429431. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1429431. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39221425 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Beat: A Multifaceted Review of Atrial Fibrillation in Sepsis: Risk Factors, Management Strategies, and Economic Impact.Cardiol Res. 2025 Feb;16(1):1-14. doi: 10.14740/cr1723. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Cardiol Res. 2025. PMID: 39897439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation and Associated Outcomes in Patients with Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Pers Med. 2022 Mar 30;12(4):547. doi: 10.3390/jpm12040547. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35455662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myeloperoxidase and its derivative hypochlorous acid combined clinical indicators predict new-onset atrial fibrillation in sepsis: a case-control study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jul 19;24(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04034-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39030470 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical predictive model of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with acute myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):439. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84759-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747552 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review on the influence of coagulopathy and immune activation on New Onset Atrial Fibrillation in patients with sepsis.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 29;20(1):e0318365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318365. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39879166 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis-induced Atrial Fibrillation: Can We Predict and Prevent This High-Risk Complication?Cureus. 2025 Jun 5;17(6):e85387. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85387. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40621331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

