MAGI1 inhibits interferon signaling to promote influenza A infection
- PMID: 36082118
- PMCID: PMC9445416
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.791143
MAGI1 inhibits interferon signaling to promote influenza A infection
Abstract
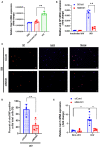
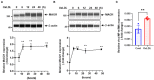
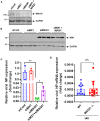
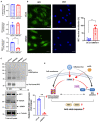
We have shown that membrane-associated guanylate kinase with inverted domain structure-1 (MAGI1), a scaffold protein with six PSD95/DiscLarge/ZO-1 (PDZ) domains, is involved in the regulation of endothelial cell (EC) activation and atherogenesis in mice. In addition to causing acute respiratory disease, influenza A virus (IAV) infection plays an important role in atherogenesis and triggers acute coronary syndromes and fatal myocardial infarction. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate the function and regulation of MAGI1 in IAV-induced EC activation. Whereas, EC infection by IAV increases MAGI1 expression, MAGI1 depletion suppresses IAV infection, suggesting that the induction of MAGI1 may promote IAV infection. Treatment of ECs with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) increases MAGI1 expression and IAV infection, suggesting that MAGI1 is part of the mechanistic link between serum lipid levels and patient prognosis following IAV infection. Our microarray studies suggest that MAGI1-depleted ECs increase protein expression and signaling networks involve in interferon (IFN) production. Specifically, infection of MAGI1-null ECs with IAV upregulates expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), interferon b1 (IFNb1), myxovirus resistance protein 1 (MX1) and 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2 (OAS2), and activate STAT5. By contrast, MAGI1 overexpression inhibits Ifnb1 mRNA and MX1 expression, again supporting the pro-viral response mediated by MAGI1. MAGI1 depletion induces the expression of MX1 and virus suppression. The data suggests that IAV suppression by MAGI1 depletion may, in part, be due to MX1 induction. Lastly, interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) translocates to the nucleus in the absence of IRF3 phosphorylation, and IRF3 SUMOylation is abolished in MAGI1-depleted ECs. The data suggests that MAGI1 inhibits IRF3 activation by maintaining IRF3 SUMOylation. In summary, IAV infection occurs in ECs in a MAGI1 expression-dependent manner by inhibiting anti-viral responses including STATs and IRF3 activation and subsequent MX1 induction, and MAGI1 plays a role in EC activation, and in upregulating a pro-viral response. Therefore, the inhibition of MAGI1 is a potential therapeutic target for IAV-induced cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: EC inflammation; IAV; IRF3; MAGI1; MX1; interferon signaling.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Abe, Chau, Wang, Vu, Reddy Velatooru, Gulraiz, Imanishi, Samanthapudi, Nguyen, Ko, Lee, Thomas, Olmsted-Davis, Kotla, Fujiwara, Cooke, Zhao, Evans and Le.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MAGI1 as a link between endothelial activation and ER stress drives atherosclerosis.JCI Insight. 2019 Apr 4;4(7):e125570. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125570. eCollection 2019 Apr 4. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30944250 Free PMC article.
-
FBXL19 in endothelial cells protects the heart from influenza A infection by enhancing antiviral immunity and reducing cellular senescence programs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):H937-H946. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00371.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39150394
-
ATG7/GAPLINC/IRF3 axis plays a critical role in regulating pathogenesis of influenza A virus.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jan 16;20(1):e1011958. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011958. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38227600 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA Lnc-MxA Inhibits Beta Interferon Transcription by Forming RNA-DNA Triplexes at Its Promoter.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00786-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00786-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31434735 Free PMC article.
-
A New Story of the Three Magi: Scaffolding Proteins and lncRNA Suppressors of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 24;13(17):4264. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174264. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503076 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Involvement of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 19;25(24):13589. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413589. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Potential Role for MAGI-1 in the Bi-Directional Relationship Between Major Depressive Disorder and Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Sep;26(9):463-483. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01223-5. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024. PMID: 38958925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNIK-driven regulation of ERK5 transcriptional activity in endothelial cells.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 2;12:1526676. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1526676. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40672381 Free PMC article.
-
Host response to influenza infections in human blood: association of influenza severity with host genetics and transcriptomic response.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 13;15:1385362. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1385362. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39192977 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

