Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through oil: Promoting full-thickness cutaneous wound healing in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections
- PMID: 36082170
- PMCID: PMC9445837
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.856651
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through oil: Promoting full-thickness cutaneous wound healing in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections
Abstract
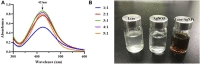
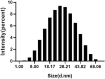
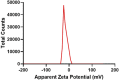
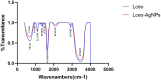
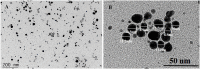
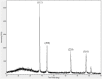
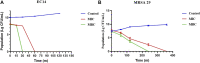
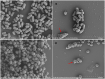
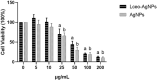
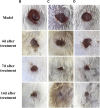
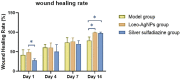
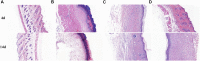
Due to the emergence of multi-drug resistant microorganisms, the development and discovery of alternative eco-friendly antimicrobial agents have become a top priority. In this study, a simple, novel, and valid green method was developed to synthesize Litsea cubeba essential oil-silver nanoparticles (Lceo-AgNPs) using Lceo as a reducing and capping agent. The maximum UV absorbance of Lceo-AgNPs appeared at 423 nm and the size was 5-15 nm through transmission electron microscopy result. The results of Fourier transform infrared and DLS showed that Lceo provided sufficient chemical bonds for Lceo-AgNPs to reinforce its stability and dispersion. The in vitro antibacterial effects of Lceo-AgNPs against microbial susceptible multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli (E. coli) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) were determined. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of Lceo-AgNPs against E. coli were 25 and 50 μg/ml. The MIC and MBC of Lceo-AgNPs against MRSA were 50 and 100 μg/ml, respectively. The results of scanning electron microscopy showed that the amount of bacteria obviously decreased and the bacteria cells were destroyed by Lceo-AgNPs. In vivo research disclosed significant wound healing and re-epithelialization effects in the Lceo-AgNPs group compared with the self-healing group and the healing activity was better than in the sulfadiazine silver group. In this experiment, Lceo-AgNPs has been shown to have effects on killing multidrug-resistant bacteria and promoting wound healing. This study suggested Lceo-AgNPs as an excellent new-type drug for wound treatment infected with multidrug-resistant bacteria, and now expects to proceed with clinical research.
Keywords: AgNPs; L. cubeba oil; antibacterial; green synthesis; multidrugresistance; wound infection.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Li, Peng, Li, Xiang, Chen, Hao, Wang, Nie, Cui, Lv, Wang, Wu, Guo and Si.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial and Wound Healing Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles From Azadirachta indica.Front Microbiol. 2021 Feb 19;12:611560. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.611560. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33679635 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles for topical applications: effect of surface coating and loading into hydrogels.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Jan 23;12:759-777. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S124294. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28176951 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial Activity of Phyto-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles From Dryopteris cristata Against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 28923 and Escherichia coli ATCC 28922.Cureus. 2024 Oct 4;16(10):e70856. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70856. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39493097 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Evaluation of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles-Kaempferol for Antibacterial Activity Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Feb 8;19:1339-1350. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S431499. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38348172 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles: Bactericidal and Mechanistic Approach against Drug Resistant Pathogens.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 1;11(2):369. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020369. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838334 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Trends in Advanced Translational Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: A Progressing Dawn of Nanotechnology.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Jan 14;14(1):47. doi: 10.3390/jfb14010047. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36662094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles against selected Gram-negative and Gram-positive pathogens.Med Pharm Rep. 2024 Jul;97(3):280-297. doi: 10.15386/mpr-2750. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Med Pharm Rep. 2024. PMID: 39234464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghila Rani K. G., Hamad M. A., Zaher D. M., Sieburth S. M., Madani N., Al-Tel T. H., et al. (2021). Drug development post COVID-19 pandemic: Toward a better system to meet current and future global health challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 16, 365–371. 10.1080/17460441.2021.1854221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahovan Z. A., Khosravimelal S., Eftekhari B. S., Mehrabi S., Hashemi A., Eftekhari S. (2020). Thermo-responsive chitosan hydrogel for healing of full-thickness wounds infected with XDR bacteria isolated from burn patients: In vitro and in vivo animal model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 164, 4475–4486. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.239 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

