Silencing RNA for MMPs May Be Utilized for Cardioprotection
- PMID: 36082193
- PMCID: PMC9433229
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9729018
Silencing RNA for MMPs May Be Utilized for Cardioprotection
Abstract
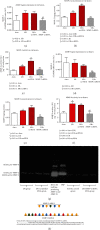
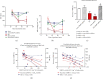
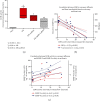
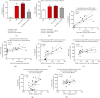
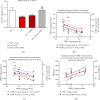
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is accompanied by an increase of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) activity, which degrades heart contractile proteins. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of MMP-2 small interfering RNA (MMP-2 siRNA) administration on I/R heart. Isolated rat hearts perfused by the Langendorff method were subjected to I/R in the presence or absence of MMP-2 siRNA. The hemodynamic parameters of heart function were monitored. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity was measured in coronary effluents. Activity and concentration of MMPs in the hearts were measured. Concentration of troponin I (TnI) in coronary effluents was examined as a target for MMP-2 degradation. Recovery of heart mechanical function was reduced after I/R; however, administration of MMP-2 siRNA resulted in restoration of proper mechanical function (p < 0.001). LDH activity was decreased after the use of MMP-2 siRNA (p = 0.02), providing evidence for reduced cardiac damage. Both MMP-2 and MMP-9 syntheses as well as their activity were inhibited in the I/R hearts after siRNA administration (p < 0.05). MMP-2 siRNA administration inhibited TnI release into the coronary effluents (p < 0.001). The use of MMP-2 siRNA contributed to the improvement of heart mechanical function and reduction of contractile proteins degradation during I/R; therefore, MMP-2 siRNA may be considered a cardioprotective agent.
Copyright © 2022 Marta Banaszkiewicz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kargiotis O., Chetty C., Gondi C. S., et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against MMP-2 mRNA results in impaired invasion and tumor-induced angiogenesis, induces apoptosis _in vitro_ and inhibits tumor growth _in vivo_ in glioblastoma. Oncogene . 2008;27(35):4830–4840. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

