High expression of Sam68 contributes to metastasis by regulating vimentin expression and a motile phenotype in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36082807
- PMCID: PMC9478953
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2022.8398
High expression of Sam68 contributes to metastasis by regulating vimentin expression and a motile phenotype in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
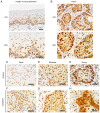
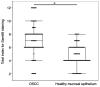
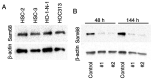
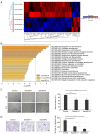
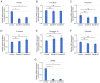
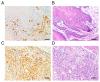
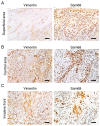
The present study aimed to investigate the clinical and biological significance of Src‑associated in mitosis 68 kDa (Sam68) in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Immunohistochemical analysis was performed on tissue samples obtained from 77 patients with OSCC. Univariate analysis revealed that the high expression of Sam68 was significantly correlated with advanced pathological T stage (P=0.01), positive lymphovascular invasion (P=0.01), and pathological cervical lymph node metastasis (P<0.01). Moreover, multivariate analysis demonstrated that the high expression of Sam68 was an independent predictive factor for cervical lymph node metastasis (odds ratio, 4.39; 95% confidence interval, 1.49‑14.23; P<0.01). These results indicated that high Sam68 expression contributed to tumor progression, especially cervical lymph node metastasis, in OSCC. mRNA sequencing was also performed to assess the changes in the transcriptome between OSCC cells with Sam68 knockdown and control cells with the aim of elucidating the biological roles of Sam68. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis revealed that downregulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were concentrated in some biological processes related to epithelial‑mesenchymal transition. Among these DEGs, it was established that vimentin was particularly downregulated in these cells. It was also confirmed that Sam68 knockdown reduced the motility of OSCC cells. Furthermore, the immunohistochemical study of vimentin identified the association between vimentin expression and Sam68 expression as well as cervical lymph node metastasis. In conclusion, the present study suggested that the high expression of Sam68 may contribute to metastasis by regulating vimentin expression and a motile mesenchymal phenotype in OSCC.
Keywords: Src‑associated in mitosis 68 kDa; epithelial‑mesenchymal transition; metastasis; motility; oral cancer; vimentin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- El-Naggar AK, Chan JKC, Grandis JR, Takata T, Slootweg PJ. 4th edition. IARC Press; Lyon: 2017. WHO classification of head and neck tumours.
-
- Sato J, Kitagawa Y, Watanabe S, Asaka T, Ohga N, Hirata K, Shiga T, Satoh A, Tamaki N. Hypoxic volume evaluated by 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography (FMISO-PET) may be a prognostic factor in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: Preliminary analyses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;47:553–560. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2017.09.007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oikawa Y, Kugimoto T, Kashima Y, Okuyama K, Ohsako T, Kuroshima T, Hirai H, Tomioka H, Shimamoto H, Michi Y, Harada H. Surgical treatment for oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study of 432 patients. Glob Health Med. 2021;3:157–162. doi: 10.35772/ghm.2020.01084. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

