Virtual Memory CD8+ T Cells: Origin and Beyond
- PMID: 36083273
- PMCID: PMC9835308
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2022.0053
Virtual Memory CD8+ T Cells: Origin and Beyond
Abstract
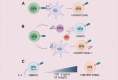
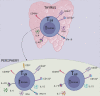
The presence of CD8+ T cells with a memory phenotype in nonimmunized mice has been noted for decades, but it was not until about 2 decades ago that they began to be studied in greater depth. Currently called virtual memory CD8+ T cells, they consist of a heterogeneous group of cells with memory characteristics, without any previous contact with their specific antigens. These cells were identified in mice, but a few years ago, a cell type with characteristics equivalent to the murine ones was described in healthy humans. In this review, we address the different aspects of its biology mainly developed in murine models and what is currently known about its cellular equivalent in humans.
Keywords: Ag-specific T cells; TIM cells; TVM cells; cancer; human TVM cells; infection.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Atherly LO, Lucas JA, Felices M, et al. 2006. The Tec family tyrosine kinases Itk and Rlk regulate the development of conventional CD8+ T cells. Immunity 25(1):79–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

