Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor
- PMID: 36083480
- PMCID: PMC9924689
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220719.001
Electroacupuncture at Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) alleviates stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome in mice by modulating gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether electroacupuncture (EA) at bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) acupoints could alleviate stress-induced irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and evaluate its effect on gut microbiota and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF).
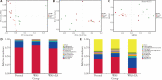
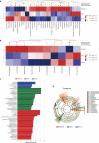
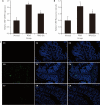
Methods: Thirty C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into the normal, water avoidance stress (WAS), and WAS+EA groups (10 mice per group). An experimental model of IBS was established by exposing the animals to WAS. The mice were treated with EA at the bilateral Tianshu (ST25) and Zusanli (ST36) acupoints. The abdominal withdrawal reflex test was conducted to evaluate visceral sensitivity in IBS. Gut microbiota was analyzed using 16S rRNA sequencing and analysis. The expression of CRF was determined using immune-ofluorescence and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
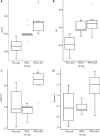
Results: EA alleviated visceral hypersensitivity in a mouse model of WAS-induced IBS. It modulated the dysbiosis of gut microbiota induced by WAS. Moreover, it suppressed the WAS-induced overexpression of CRF in colon tissues.
Conclusion: The findings of this study suggest that EA alleviated WAS-induced IBS mechanisms possibly involving the modulation of the dysbiosis of gut microbiota and suppression of CRF expression.
Keywords: corticotropin-releasing hormone; electroacupuncture; gastrointestinal microbiome; irritable bowel syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Sultan S, Malhotra A. . Irritable bowel syndrome. Ann Intern Med 2017; 166: ITC81-96. - PubMed
-
- Canavan C, West J, Card T. . Review article: the economic impact of the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014; 40: 1023-34. - PubMed
-
- Koloski NA, Jones M, Talley NJ. . Evidence that independent gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut pathways operate in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia: a 1-year population-based prospective study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2016; 44: 592-600. - PubMed
-
- Gué M, Del Rio-Lacheze C, Eutamene H, Théodorou V, Fioramonti J, Buéno L. . Stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity to rectal distension in rats: role of CRF and mast cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil 1997; 9: 271-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

