Role of adropin in arterial stiffening associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 36083795
- PMCID: PMC9602697
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00385.2022
Role of adropin in arterial stiffening associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
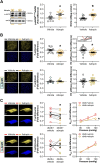
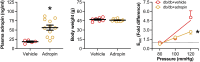
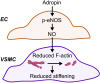
Adropin is a peptide largely secreted by the liver and known to regulate energy homeostasis; however, it also exerts cardiovascular effects. Herein, we tested the hypothesis that low circulating levels of adropin in obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D) contribute to arterial stiffening. In support of this hypothesis, we report that obesity and T2D are associated with reduced levels of adropin (in liver and plasma) and increased arterial stiffness in mice and humans. Establishing causation, we show that mesenteric arteries from adropin knockout mice are also stiffer, relative to arteries from wild-type counterparts, thus recapitulating the stiffening phenotype observed in T2D db/db mice. Given the above, we performed a set of follow-up experiments, in which we found that 1) exposure of endothelial cells or isolated mesenteric arteries from db/db mice to adropin reduces filamentous actin (F-actin) stress fibers and stiffness, 2) adropin-induced reduction of F-actin and stiffness in endothelial cells and db/db mesenteric arteries is abrogated by inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) synthase, and 3) stimulation of smooth muscle cells or db/db mesenteric arteries with a NO mimetic reduces stiffness. Lastly, we demonstrated that in vivo treatment of db/db mice with adropin for 4 wk reduces stiffness in mesenteric arteries. Collectively, these findings indicate that adropin can regulate arterial stiffness, likely via endothelium-derived NO, and thus support the notion that "hypoadropinemia" should be considered as a putative target for the prevention and treatment of arterial stiffening in obesity and T2D.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Arterial stiffening, a characteristic feature of obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), contributes to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Herein we establish that adropin is decreased in obese and T2D models and furthermore provide evidence that reduced adropin may directly contribute to arterial stiffening. Collectively, findings from this work support the notion that "hypoadropinemia" should be considered as a putative target for the prevention and treatment of arterial stiffening in obesity and T2D.
Keywords: adropin; endothelial cells; mesenteric arteries; nitric oxide; smooth muscle cellss.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Mattace-Raso FUS, van der Cammen TJM, Hofman A, van Popele NM, Bos ML, Schalekamp MADH, Asmar R, Reneman RS, Hoeks APG, Breteler MMB, Witteman JCM. Arterial stiffness and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: the Rotterdam Study. Circulation 113: 657–663, 2006. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.555235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Townsend RR, Wilkinson IB, Schiffrin EL, Avolio AP, Chirinos JA, Cockcroft JR, Heffernan KS, Lakatta EG, McEniery CM, Mitchell GF, Najjar SS, Nichols WW, Urbina EM, Weber T; American Heart Association Council on Hypertension. Recommendations for improving and standardizing vascular research on arterial stiffness: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 66: 698–722, 2015. doi: 10.1161/HYP.0000000000000033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar KG, Trevaskis JL, Lam DD, Sutton GM, Koza RA, Chouljenko VN, Kousoulas KG, Rogers PM, Kesterson RA, Thearle M, Ferrante AW Jr, Mynatt RL, Burris TP, Dong JZ, Halem HA, Culler MD, Heisler LK, Stephens JM, Butler AA. Identification of adropin as a secreted factor linking dietary macronutrient intake with energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Cell Metab 8: 468–481, 2008. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.10.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

