Effect of systemic arterial hypertension and use of antiproteinuric drug in induction therapy for lupus nephritis
- PMID: 36083852
- PMCID: PMC7453831
- DOI: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2020AO5322
Effect of systemic arterial hypertension and use of antiproteinuric drug in induction therapy for lupus nephritis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the therapeutic response to induction treatment in lupus nephritis patients.
Methods: A total of 29 patients diagnosed with systemic lupus erythematosus and biopsy-proven nephritis were divided into two groups, one with hypertensive individuals and another non-hypertensive patients. The hypertensive patients included were on drugs with antiproteinuric effect. The induction treatment comprised mycophenolate mofetil or cyclophosphamide, based on 24-hour proteinuria and serum creatinine parameters for therapeutic evaluation after 6 months of intervention. The retrospective evaluation of the follow-up was made based on information collected from the medical records.
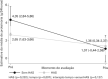
Results: Patients with and without hypertension presented similar behaviors of proteinuria (p=0.127) and creatinine (p=0.514) over time. For proteinuria, only the time effect (p=0.007), but not hypertensive effect (p=0.232), was found. There was a reduction in proteinuria levels (reduction by 3.28g/24 hours, on average) from the beginning to the final measurement. As to creatinine, no hypertensive (p=0.757) or time (p=0.154) effects were found.
Conclusion: Similarity in behavior of proteinuria was observed, after induction treatment for nephritis, taking into account the hypertensive effect. The prior condition did not hinder these patients reaching the recommended proteinuria goal.
Objetivo: Avaliar resposta terapêutica a tratamento de indução de pacientes com nefrite lúpica.
Métodos: Foram divididos em dois grupos 29 pacientes com diagnóstico de lúpus eritematoso sistêmico e nefrite comprovada por biópsia, sendo um de portadores de hipertensão e outro sem essa comorbidade. Dentre os hipertensos, foram incluídos aqueles que faziam uso de antiproteinúrico. O tratamento de indução foi realizado com micofenolato de mofetila ou ciclofosfamida, sendo utilizados os parâmetros de proteinúria de 24 horas e creatinina sérica para avaliação terapêutica após 6 meses da intervenção. A avaliação retrospectiva do seguimento foi realizada a partir de informações coletadas de prontuário.
Resultados: Pacientes com e sem hipertensão apresentaram comportamentos similares de proteinúria (p=0,127) e creatinina (p=0,514) ao longo do tempo. Para a proteinúria, observou-se apenas o efeito de tempo (p=0,007), mas não de hipertensão (p=0,232). Houve redução nos níveis da proteinúria (redução de 3,28g/24 horas, em média) do início para o momento pós. Já para a creatinina, não se observou efeito de hipertensão (p=0,757) e tampouco de tempo (p=0,154).
Conclusão: Observamos similaridade no comportamento da proteinúria, após tratamento de indução para nefrite, levando em conta o efeito hipertensão. A comorbidade prévia não se mostrou impeditiva para que estes pacientes atingissem a meta de proteinúria preconizada.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Induction therapy and outcome of proliferative lupus nephritis in the top end of Northern Australia - a single centre study retrospective study.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Jul 4;23(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02849-w. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35787253 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Outcomes Observed among Biopsy Proven Lupus Nephritis Patients Treated with Mycophenolate Mofetil as First-line Therapy.Cureus. 2017 Dec 4;9(12):e1907. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1907. Cureus. 2017. PMID: 29410944 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive factors for low rate of remission in a population of Colombian patients with severe proliferative lupus nephritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2015 May;34(5):897-903. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2864-7. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25592376
-
Rituximab use as induction therapy for lupus nephritis: a systematic review.Lupus. 2020 Jul;29(8):892-912. doi: 10.1177/0961203320928412. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Lupus. 2020. PMID: 32486934
-
[Lupus nephritis].Nephrol Ther. 2019 Jun;15(3):174-189. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2018.11.003. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Nephrol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30738732 Review. French.
References
-
- 2. Ortega LM, Schultz DR, Lenz O, Pardo V, Contreras GN. Review: Lupus nephritis: pathologic features, epidemiology and a guide to therapeutic decisions. Lupus. 2010;19(5):557-74. Review. - PubMed
- Ortega LM, Schultz DR, Lenz O, Pardo V, Contreras GN. Review: Lupus nephritis: pathologic features, epidemiology and a guide to therapeutic decisions. Lupus. 2010;19(5):557–574. Review. - PubMed
-
- 3. Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L, Manzi S, Ginzler E, Gladman DD, et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2550-7. - PubMed
- Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L, Manzi S, Ginzler E, Gladman DD, et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2550–2557. - PubMed
-
- 4. Klumb EM, Silva CA, Lanna CC, Sato EI, Borba EF, Brenol JC, et al. Consensus of the Brazilian Society of Rheumatology for the diagnosis, management and treatment of lupus nephritis. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2015;55(1):1-21. - PubMed
- Klumb EM, Silva CA, Lanna CC, Sato EI, Borba EF, Brenol JC, et al. Consensus of the Brazilian Society of Rheumatology for the diagnosis, management and treatment of lupus nephritis. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2015;55(1):1–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

