Perspective: Human Milk Composition and Related Data for National Health and Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research
- PMID: 36084013
- PMCID: PMC9776678
- DOI: 10.1093/advances/nmac099
Perspective: Human Milk Composition and Related Data for National Health and Nutrition Monitoring and Related Research
Abstract
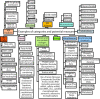
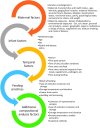
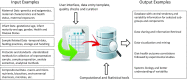
National health and nutrition monitoring is an important federal effort in the United States and Canada, and the basis for many of their nutrition and health policies. Understanding of child exposures through human milk (HM) remains out of reach due to lack of current and representative data on HM's composition and intake volume. This article provides an overview of the current national health and nutrition monitoring activities for HM-fed children, HM composition (HMC) and volume data used for exposure assessment, categories of potential measures in HM, and associated variability factors. In this Perspective, we advocate for a framework for collection and reporting of HMC data for national health and nutrition monitoring and programmatic needs, including a shared vision for a publicly available Human Milk Composition Data Repository (HMCD-R) to include essential metadata associated with HMC. HMCD-R can provide a central, integrated platform for researchers and public health officials for compiling, evaluating, and sharing HMC data. The compiled compositional and metadata in HMCD-R would provide pertinent measures of central tendency and variability and allow use of modeling techniques to approximate compositional profiles for subgroups, providing more accurate exposure assessments for purposes of monitoring and surveillance. HMC and related metadata could facilitate understanding the complexity and variability of HM composition, provide crucial data for assessment of infant and maternal nutritional needs, and inform public health policies, food and nutrition programs, and clinical practice guidelines.
Keywords: B-24 population; bioactives in human milk; breast milk; environmental chemicals in human milk; human milk; human milk composition data repository (HMCD-R); intake volume; national monitoring; nutrients in human milk; variability in human milk.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society for Nutrition 2022.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . The optimal duration of exclusive breastfeeding: report of the expert consultation. [Internet]. 2001; [cited 2022 Aug 25]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/nutrition/publications/infantfeeding/WHO_NHD_01.09/....
-
- Eidelman AI, Schanler RJ. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827–41. - PubMed
-
- Vorosmarti A, Yaktine AL, Rasmussen K. Scanning for new evidence on the nutrient content of human milk: a process model for determining age-specific nutrient requirements. [Internet]. 2020; [cited 2022 Aug 25]. Available from: https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/25943/scanning-for-new-evidenc.... - PubMed

