CCT196969 effectively inhibits growth and survival of melanoma brain metastasis cells
- PMID: 36084109
- PMCID: PMC9462752
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273711
CCT196969 effectively inhibits growth and survival of melanoma brain metastasis cells
Abstract
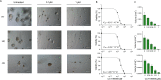
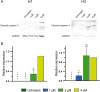
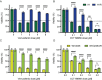
Melanomas frequently metastasize to the brain. Despite recent progress in the treatment of melanoma brain metastasis, therapy resistance and relapse of disease remain unsolved challenges. CCT196969 is a SRC family kinase (SFK) and Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (RAF) inhibitor with documented effects in primary melanoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Using in vitro cell line assays, we studied the effects of CCT196969 in multiple melanoma brain metastasis cell lines. The drug effectively inhibited proliferation, migration, and survival in all examined cell lines, with viability IC50 doses in the range of 0.18-2.6 μM. Western blot analysis showed decreased expression of p-ERK, p-MEK, p-STAT3 and STAT3 upon CCT196969 treatment. Furthermore, CCT196969 inhibited viability in two B-Raf Proto-Oncogene (BRAF) inhibitor resistant metastatic melanoma cell lines. Further in vivo studies should be performed to determine the treatment potential of CCT196969 in patients with treatment-naïve and resistant melanoma brain metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Chason J.L., Walker F.B., and Landers J.W., Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer, 1963. 16: p. 781–7. - PubMed
-
- Davies M.A., et al.., Prognostic factors for survival in melanoma patients with brain metastases. Cancer, 2011. 117(8): p. 1687–96. - PubMed
-
- Budman D.R., Camacho E., and Wittes R.E., The current causes of death in patients with malignant melanoma. Eur J Cancer, 1978. 14(4): p. 327–30. - PubMed
-
- Lagerwaard F.J., et al.., Identification of prognostic factors in patients with brain metastases: a review of 1292 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1999. 43(4): p. 795–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

