Liberation From Mechanical Ventilation Before Decannulation From Venovenous Extracorporeal Life Support in Severe COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 36084294
- PMCID: PMC9949369
- DOI: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001806
Liberation From Mechanical Ventilation Before Decannulation From Venovenous Extracorporeal Life Support in Severe COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
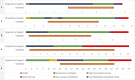
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has been associated with the significant use of venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VVECMO) globally. Identifying strategies to optimize care is essential to improving patient important outcomes. By liberation from mechanical ventilation (MV) before VVECMO to provide awake-ECMO, complications related to MV could be minimized, leading to improved outcomes. Between March 2020 and October 2021, we conducted a prospective observational study at the Kuwait Extracorporeal Life Support Program, of patients admitted for COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), with recording baseline characteristics, respiratory support, and ECMO parameters. Of the 207 patients who underwent VVECMO for COVID-19 ARDS during this period, only 5 patients were successfully liberated from MV before decannulation to provide awake-ECMO. Four were female with a median age of 38. Before VVECMO, all patients received corticosteroids and lung-protective ventilation with four receiving prone positioning. The median duration of MV use was 4 days, whereas the median duration of VVECMO use was 12 days, with early mobility, and all survived until hospital discharge. The safety and feasibility of liberation from MV before ECMO decannulation to provide awake-ECMO were demonstrated, but further studies are warranted to identify factors associated with this success.
Copyright © ASAIO 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- WHO International. 2021. Timeline: WHO’s COVID-19 response. Available at: <https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/interact...>.Accessed 23 September 2021.
-
- Hayes K, Holland AE, Pellegrino VA, Young M, Paul E, Hodgson CL: Early rehabilitation during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation has minimal impact on physiological parameters: a pilot randomised controlled trial. Aust Crit Care 34: 217–225, 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

