Lysosomal Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease: Insights From LRRK2 and GBA1 Rodent Models
- PMID: 36085537
- PMCID: PMC10119359
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-022-01290-z
Lysosomal Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease: Insights From LRRK2 and GBA1 Rodent Models
Abstract
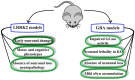
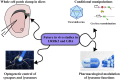
The discovery of mutations in LRRK2 and GBA1 that are linked to Parkinson's disease provided further evidence that autophagy and lysosome pathways are likely implicated in the pathogenic process. Their protein products are important regulators of lysosome function. LRRK2 has kinase-dependent effects on lysosome activity, autophagic efficacy and lysosomal Ca2+ signaling. Glucocerebrosidase (encoded by GBA1) is a hydrolytic enzyme contained in the lysosomes and contributes to the degradation of alpha-synuclein. PD-related mutations in LRRK2 and GBA1 slow the degradation of alpha-synuclein, thus directly implicating the dysfunction of the process in the neuropathology of Parkinson's disease. The development of genetic rodent models of LRRK2 and GBA1 provided hopes of obtaining reliable preclinical models in which to study pathogenic processes and perform drug validation studies. Here, I will review the extensive characterization of these models, their impact on understanding lysosome alterations in the course of Parkinson's disease and what novel insights have been obtained. In addition, I will discuss how these models fare with respect to the features of a "gold standard" animal models and what could be attempted in future studies to exploit LRRK2 and GBA1 rodent models in the fight against Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Animal models; Glucocerebrosidase; LRRK2; Lysosomes; Neuropathology; Parkinson’s disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Langston JW, Langston EB, Irwin I. MPTP-induced parkinsonism in human and non-human primates–clinical and experimental aspects. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1984;100:49–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

