Computationally efficient neural network classifiers for next generation closed loop neuromodulation therapy - a case study in epilepsy
- PMID: 36085909
- PMCID: PMC7613668
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC48229.2022.9871793
Computationally efficient neural network classifiers for next generation closed loop neuromodulation therapy - a case study in epilepsy
Abstract
This work explores the potential utility of neural network classifiers for real- time classification of field-potential based biomarkers in next-generation responsive neuromodulation systems. Compared to classical filter-based classifiers, neural networks offer an ease of patient-specific parameter tuning, promising to reduce the burden of programming on clinicians. The paper explores a compact, feed - forward neural network architecture of only dozens of units for seizure-state classification in refractory epilepsy. The proposed classifier offers comparable accuracy to filter- classifiers on clinician-labeled data, while reducing detection latency. As a trade-off to classical methods, the paper focuses on keeping the complexity of the architecture minimal, to accommodate the on-board computational constraints of implantable pulse generator systems. Clinical relevance-A neural network-based classifier is presented for responsive neurostimulation, with comparable accuracy to classical methods at reduced latency.
Figures


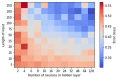
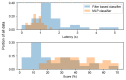
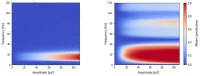
References
-
- Gotman J, Gloor P. Automatic recognition and quantification of interictal epileptic activity in the human scalp EEG. Clin Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;41(5):513–529. - PubMed
-
- Osorio I, Frei MG, Wilkinson SB. Real-time automated detection and quantitative analysis of seizures and short-term prediction of clinical onset. Epilepsia. 1998 Jun;39(6):615–627. - PubMed
-
- Osorio I, et al. Performance reassessment of a real-time seizuredetection algorithm on long ECoG series. Epilepsia. 2002 Dec;43(12):1522–1535. - PubMed
-
- Bhavaraju N, Frei M, Osorio I. Analog seizure detection and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2006 Feb;53(2):238–245. - PubMed
-
- Sun FT, Morrell MJ. The RNS system: responsive cortical stimulation for the treatment of refractory partial epilepsy. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2014 Nov;11(6):563–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
