Characterization of a Temporary Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Electrode Utilizing a Bioabsorbable Suture Substrate
- PMID: 36086486
- PMCID: PMC10369404
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC48229.2022.9871604
Characterization of a Temporary Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Electrode Utilizing a Bioabsorbable Suture Substrate
Abstract
Electrical stimulation after peripheral nerve injury (PNI) has the potential to promote more rapid and complete recovery of damaged fiber tracts. While permanently implanted devices are commonly used to treat chronic or persistent conditions, they are not ideal solutions for transient medical therapies due to high costs, increased risk of surgical injury, irritation, infection, and persistent inflammation at the site of the implant. Furthermore, removal of temporary leads placed on or around peripheral nerves may have unacceptable risk for nerve injury, which is counterproductive in developing therapies for PNI treatment. Transient devices which provide effective clinical stimulation while being capable of harmless bioabsorption may overcome key challenges in these areas. However, current bioabsorbable devices are limited in their robustness and require complex fabrication strategies and novel materials which may complicate their clinical translation pathway. In this study, we present a simple bioabsorbable / biodegradable electrode fabricated by modifying standard absorbable sutures, and we present data characterizing our prototype's stability in vitro and in vivo.
Figures

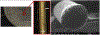

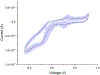
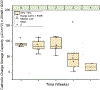

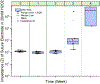

References
-
- Tapp M, Wenzinger E, Tarabishy S, Ricci J, & Herrera FA (2019). The epidemiology of upper extremity nerve injuries and associated cost in the US Emergency Departments. Annals of plastic surgery, 83(6), 676–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
