Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated gene signature to predict the immune status and prognosis of cutaneous melanoma
- PMID: 36086718
- PMCID: PMC10980369
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030280
Identification of an endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated gene signature to predict the immune status and prognosis of cutaneous melanoma
Abstract
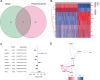
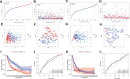
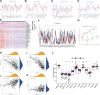
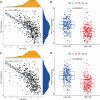
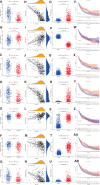
Besides protecting normal cells from various internal and external perturbations, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is also directly related to the pathogenesis of cutaneous melanoma (CM). However, due to the lack of specific molecular biomarkers, ER stress has not been considered a novel treatment target for CM. Here, we identified ER stress-related genes involved in the prognosis of CM patients and constructed an effective model for the prognostic prediction of these patients. First, gene expression data of CM and normal skin tissues from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) databases were retrieved to identify differentially expressed ER stress-related genes in CM. Meanwhile, an independent cohort obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database was used for validation. The ER stress genes (ZBP1, DIABLO, GNLY, FASLG, AURKA, TNFRSF21, and CD40LG) that were associated with CM prognosis were incorporated into our prognostic model. The functional analyses indicated that the prognostic model was correlated with patient survival, gender, and cancer growth. Multivariate and univariate Cox regressions revealed that the constructed model could serve as an independent prognostic factor for CM patients. The pathway enrichment analysis showed that the risk model was enriched in different immunity and cancer progression-associated pathways. Moreover, the signature model was significantly connected with the immune subtypes, infiltration of immune cells, immune microenvironment, as well as tumor stem cells. The gene function analysis revealed that 7 ER stress genes were differentially expressed in CM patients and were significantly associated with prognosis and several antitumor drugs. Overall, our current model presented predictive value for the prognosis of CM patients and can be further used in the development of novel therapeutic strategies for CM.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ekwueme DU, Guy GP, Jr., Li C, et al. The health burden and economic costs of cutaneous melanoma mortality by race/ethnicity-United States, 2000 to 2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 Suppl 1):S133–43. - PubMed
-
- Kanavy HE, Gerstenblith MR. Ultraviolet radiation and melanoma. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:222–8. - PubMed
-
- Pawlikowska M, Piotrowski J, Jędrzejewski T, et al. Coriolus versicolor-derived protein-bound polysaccharides trigger the caspase-independent cell death pathway in amelanotic but not melanotic melanoma cells. Phytother Res. 2020;34:173–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

