Activation and expansion of presynaptic signaling foci drives presynaptic homeostatic plasticity
- PMID: 36087584
- PMCID: PMC9671843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.08.016
Activation and expansion of presynaptic signaling foci drives presynaptic homeostatic plasticity
Abstract
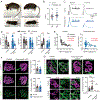
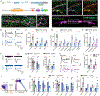
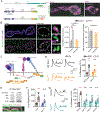
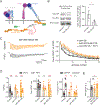
Presynaptic homeostatic plasticity (PHP) adaptively regulates synaptic transmission in health and disease. Despite identification of numerous genes that are essential for PHP, we lack a dynamic framework to explain how PHP is initiated, potentiated, and limited to achieve precise control of vesicle fusion. Here, utilizing both mice and Drosophila, we demonstrate that PHP progresses through the assembly and physical expansion of presynaptic signaling foci where activated integrins biochemically converge with trans-synaptic Semaphorin2b/PlexinB signaling. Each component of the identified signaling complexes, including alpha/beta-integrin, Semaphorin2b, PlexinB, talin, and focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and their biochemical interactions, are essential for PHP. Complex integrity requires the Sema2b ligand and complex expansion includes a ∼2.5-fold expansion of active-zone associated puncta composed of the actin-binding protein talin. Finally, complex pre-expansion is sufficient to accelerate the rate and extent of PHP. A working model is proposed incorporating signal convergence with dynamic molecular assemblies that instruct PHP.
Keywords: ALS; FAK; Plexin; homeostatic plasticity; integrin; neuromuscular junction; neuroprotection; semaphorin; synaptic plasticity; talin.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests G.W.D. is a member of the Advisory Board of the journal Neuron.
Figures

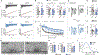
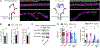

Comment in
-
Homing in on homeostatic plasticity.Neuron. 2022 Nov 16;110(22):3645-3647. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.10.033. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 36395749
References
-
- Babayan AH, Kramár EA, Barrett RM, Jafari M, Häettig J, Chen LY, Rex CS, Lauterborn JC, Wood MA, Gall CM, & Lynch G (2012). Integrin dynamics produce a delayed stage of long-term potentiation and memory consolidation. Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 12854–12861. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2024-12.2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

