The potential pathogenic roles of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 in patients with MPO-ANCA-positive vasculitis
- PMID: 36088289
- PMCID: PMC9464401
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-022-00513-4
The potential pathogenic roles of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 in patients with MPO-ANCA-positive vasculitis
Abstract
Background: The significance of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) has not been clarified. This study was dedicated to exploring the potential pathogenic roles of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 in patients with myeloperoxidase (MPO)-ANCA-positive vasculitis.
Methods: Serum and urine concentrations of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 of forty-two AAV patients were evaluated. The influence of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 on the chemotaxis, the apoptosis, the release of IL-1β, the complement activation, the respiratory burst, as well as the neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation of MPO-ANCA-activated neutrophils was investigated.
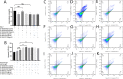
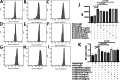
Results: The serum and urine S100A8/A9 and S100A12 of active MPO-AAV significantly increased (compared with inactive AAV and healthy controls, p < 0.001) and were correlated with the severity of the disease. In vitro study showed that S100A8/A9 and S100A12 activated the p38 MAPK/NF-κB p65 pathway, increased the chemotaxis index (CI) and the release of IL-1β, extended the life span, and enhanced the complement activation ability of MPO-ANCA-activated neutrophils. The Blockade of TLR4 and RAGE inhibited the effects of S100A8/A9 and S100A12. All above-mentioned effects of S100A8/A9 and S100A12 were ROS-independent because neither S100A8/A9 nor S100A12 enhanced the ROS formation and NETs formation of MPO-ANCA-activated neutrophils.
Conclusion: S100A8/A9 and S100A12 serve as markers for assessing the disease severity, and they may also play a role in MPO-AAV pathogenesis.
Keywords: AAV; ANCA; MPO; S100A12; S100A8/A9.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Schonermarck U, Csernok E, Gross WL. Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: challenges and solutions 2014. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30(Suppl 1):i46–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

