The roles of intratumour heterogeneity in the biology and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36088504
- PMCID: PMC9568427
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-022-02448-x
The roles of intratumour heterogeneity in the biology and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
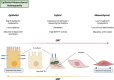
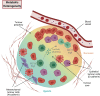
Intratumour heterogeneity (ITH) has become an important focus of cancer research in recent years. ITH describes the cellular variation that enables tumour evolution, including tumour progression, metastasis and resistance to treatment. The selection and expansion of genetically distinct treatment-resistant cancer cell clones provides one explanation for treatment failure. However, tumour cell variation need not be genetically encoded. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) in particular, the complex tumour microenvironment as well as crosstalk between tumour and stromal cells result in exceptionally variable tumour cell phenotypes that are also highly adaptable. In this review we discuss four different types of phenotypic heterogeneity within PDAC, from morphological to metabolic heterogeneity. We suggest that these different types of ITH are not independent, but, rather, can inform one another. Lastly, we highlight recent findings that suggest how therapeutic efforts may halt PDAC progression by constraining cellular heterogeneity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Pourshams A, Sepanlou SG, Ikuta KS, Bisignano C, Safiri S, Roshandel G, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:934–47. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30347-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

