Effects of ultrasonic treatment on ovomucin: Structure, functional properties and bioactivity
- PMID: 36088894
- PMCID: PMC9474920
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106153
Effects of ultrasonic treatment on ovomucin: Structure, functional properties and bioactivity
Abstract
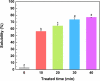
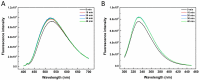
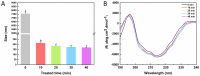
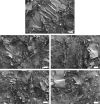
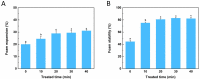
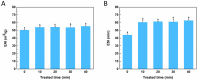
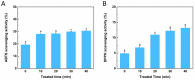
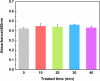
The effects of ultrasonic treatment on the structure, functional properties and bioactivity of Ovomucin (OVM) were investigated in this study. Ultrasonic treatment could significantly enhance OVM solubility without destroying protein molecules. The secondary structure changes, including β-sheet reduction and random coil increase, indicate more disorder in OVM structure. After ultrasonic treatment, the OVM molecule was unfolded partially, resulting in the exposure of hydrophobic regions. The changes in OVM molecules led to an increase in intrinsic fluorescence and surface hydrophobicity. By detecting the particle size of protein solution, it was confirmed that ultrasonic treatment disassembled the OVM aggregations causing a smaller particle size. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images showed that ultrasonic cavitation significantly reduced the tendency of OVM to form stacked lamellar structure. Those changes in structure resulted in the improvement of foaming, emulsification and antioxidant capacity of OVM. Meanwhile, the detection results of ELISA showed that ultrasonic treatment did not change the biological activity of OVM. These results suggested that the relatively gentle ultrasound treatment could be utilized as a potential approach to modify OVM for property improvement.
Keywords: Bioactivity; Function properties; Ovomucin; Solubility; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Wang Z., Tu A., Tang D., Shan Y. Effectively preparing soluble ovomucin with high antiviral activity from egg white. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018;118:504–510. - PubMed
-
- Sun X., Gänzle M., Wu J. Glycopeptides from egg white ovomucin inhibit K88ac enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli adhesion to porcine small intestinal epithelial cell-line. J. Funct. Foods. 2019;54:320–328.
-
- Sun X., Chakrabarti S., Fang J., Yin Y., Wu J.J.N.R. Low-molecular-weight fractions of Alcalase hydrolyzed egg ovomucin extract exert anti-inflammatory activity in human dermal fibroblasts through the inhibition of tumor necrosis factor–mediated nuclear factor κB pathway. Nutr. Res. 2016;36:648–657. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

