Whole-liver enhanced CT radiomics analysis to predict metachronous liver metastases after rectal cancer surgery
- PMID: 36089623
- PMCID: PMC9465956
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-022-00485-z
Whole-liver enhanced CT radiomics analysis to predict metachronous liver metastases after rectal cancer surgery
Abstract
Background: To develop a radiomics model based on pretreatment whole-liver portal venous phase (PVP) contrast-enhanced CT (CE-CT) images for predicting metachronous liver metastases (MLM) within 24 months after rectal cancer (RC) surgery.
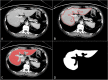
Methods: This study retrospectively analyzed 112 RC patients without preoperative liver metastases who underwent rectal surgery between January 2015 and December 2017 at our institution. Volume of interest (VOI) segmentation of the whole-liver was performed on the PVP CE-CT images. All 1316 radiomics features were extracted automatically. The maximum-relevance and minimum-redundancy and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator methods were used for features selection and radiomics signature constructing. Three models based on radiomics features (radiomics model), clinical features (clinical model), and radiomics combined with clinical features (combined model) were built by multivariable logistic regression analysis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to assess the diagnostic performance of models, and calibration curve and the decision curve analysis were performed to evaluate the clinical application value.
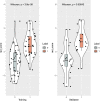
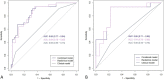
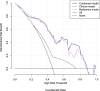
Results: In total, 52 patients in the MLM group and 60 patients in the non-MLM group were enrolled in this study. The radscore was built using 16 selected features and the corresponding coefficients. Both the radiomics model and the combined model showed higher diagnostic performance than clinical model (AUCs of training set: radiomics model 0.84 (95% CI, 0.76-0.93), clinical model 0.65 (95% CI, 0.55-0.75), combined model 0.85 (95% CI, 0.77-0.94); AUCs of validation set: radiomics model 0.84 (95% CI, 0.70-0.98), clinical model 0.58 (95% CI, 0.40-0.76), combined model 0.85 (95% CI, 0.71-0.99)). The calibration curves showed great consistency between the predicted value and actual event probability. The DCA showed that both the radiomics and combined models could add a net benefit on a large scale.
Conclusions: The radiomics model based on preoperative whole-liver PVP CE-CT could predict MLM within 24 months after RC surgery. Clinical features could not significantly improve the prediction efficiency of the radiomics model.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Liver metastases; Radiomics; Rectal cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

