Biopolymer coating for particle surface engineering and their biomedical applications
- PMID: 36090610
- PMCID: PMC9450159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100407
Biopolymer coating for particle surface engineering and their biomedical applications
Abstract
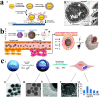
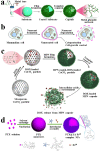
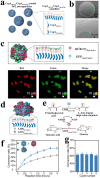
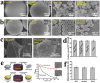
Surface engineering of particles based on a polymeric coating is of great interest in materials design and applications. Due to the disadvantages of non-biodegradability and undesirable biocompatibility, the application of petroleum-based synthetic polymers coating in the biomedical field has been greatly limited. In addition, there is lack of a universal surface modification method to functionalize particles of different compositions, sizes, shapes, and structures. Thus, it is imperative to develop a versatile biopolymeric coating with good biocompatibility and tunable biodegradability for the preparation of functional particle materials regardless of their surface chemical and physical structures. Recently, the natural polysaccharide polymers (e.g. chitosan and cellulose), polyphenol-based biopolymers (e.g. polydopamine and tannic acid), and proteins (e.g. amyloid-like aggregates) have been utilized in surface modification of particles, and applications of these modified particles in the field of biomedicine have been also intensively exploited. In this review, the preparation of the above three coatings on particles surface are summarized, and the applications of these materials in drug loading/release, biomineralization, cell immobilization/protection, enzyme immobilization/protection, and antibacterial/antiviral are exemplified. Finally, the challenges and the future research directions on biopolymer coating for particles surface engineering are prospected.
Keywords: Amyloid-like protein aggregates; Bio-applications; Biopolymer; Particle; Surface engineering.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
One-Step Assembly of a Biomimetic Biopolymer Coating for Particle Surface Engineering.Adv Mater. 2018 Sep;30(38):e1802851. doi: 10.1002/adma.201802851. Epub 2018 Aug 5. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 30079540
-
Techniques, applications and prospects of polysaccharide and protein based biopolymer coatings: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;266(Pt 2):131104. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131104. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38522703 Review.
-
[Advances in polydopamine surface modification for capillary electrochromatography].Se Pu. 2020 Sep 8;38(9):1057-1068. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2020.03004. Se Pu. 2020. PMID: 34213272 Chinese.
-
A Review of Water-Resistant Cellulose-Based Materials in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Application.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(40):8296-8318. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210208113354. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33557729 Review.
-
Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Films Based on Natural Polymers: From Fundamentals to Bio-Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jul 9;13(14):2254. doi: 10.3390/polym13142254. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34301010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of an HBPL antibacterial coating on a phase-transition lysozyme-modified titanium surface.Front Oral Health. 2025 Jun 27;6:1615280. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1615280. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40655934 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of PCL/CMARX/GO Composite Nanofibrous Mats for Dye Adsorption: Wastewater Treatment.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Jun 26;13(7):622. doi: 10.3390/membranes13070622. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504988 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and Antifungal Tannic Acid Coating on Plasma-Activated Titanium Alloy Surface.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 22;26(15):7051. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157051. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806180 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer Coated Functional Catalysts for Industrial Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Apr 24;15(9):2009. doi: 10.3390/polym15092009. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37177157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymer-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Quercetin Delivery: A Potential Strategy for Colon Cancer Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 3;17(4):467. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040467. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Decher G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science. 1997;277(5330):1232–1237.
-
- Caruso F., Caruso R.A., Mohwald H. Nanoengineering of inorganic and hybrid hollow spheres by colloidal templating. Science. 1998;282(5391):1111–1114. - PubMed
-
- Ryu D.Y., Shin K., Drockenmuller E., et al. A generalized approach to the modification of solid surfaces. Science. 2005;308(5719):236–239. - PubMed
-
- Gupta A.K., Gupta M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2005;26(18):3995–4021. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

