Identification and characterization of a MAPT-targeting locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotide therapeutic for tauopathies
- PMID: 36090761
- PMCID: PMC9424863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.07.027
Identification and characterization of a MAPT-targeting locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotide therapeutic for tauopathies
Abstract
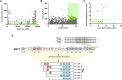
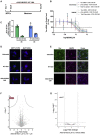
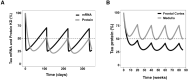
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein (MAPT, tau) implicated in the pathogenesis of tauopathies, a spectrum of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by accumulation of hyperphosphorylated, aggregated tau. Because tau pathology can be distinct across diseases, a pragmatic therapeutic approach may be to intervene at the level of the tau transcript, as it makes no assumptions to mechanisms of tau toxicity. Here we performed a large library screen of locked-nucleic-acid (LNA)-modified antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), where careful tiling of the MAPT locus resulted in the identification of hot spots for activity in the 3' UTR. Further modifications to the LNA design resulted in the generation of ASO-001933, which selectively and potently reduces tau in primary cultures from hTau mice, monkey, and human neurons. ASO-001933 was well tolerated and produced a robust, long-lasting reduction in tau protein in both mouse and cynomolgus monkey brain. In monkey, tau protein reduction was maintained in brain for 20 weeks post injection and corresponded with tau protein reduction in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Our results demonstrate that LNA-ASOs exhibit excellent drug-like properties and sustained efficacy likely translating to infrequent, intrathecal dosing in patients. These data further support the development of LNA-ASOs against tau for the treatment of tauopathies.
Keywords: MAPT; MT: oligonucleotides: therapies and applications; antisense oligonucleotides; cynomolgus monkey; intrathecal; locked nucleic acids; neurodegeneration; tau; tauopathies.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
C.M.K., J.K.L., R.S., Y.B., D.D., S.E.M., and R.E.O. are employees of BMS and own stock or restricted stock units in BMS. A.E., Y. Li, Y. Lu, J.E. Meredith, J.E. Macor, M.W., V.W., K.J., M.G., J.M.B., L.H., A.F., J.P., M.B., A.B., J.E.M., C.F.A., and A.M.C. were employees of BMS when the work described was carried out. R.E.O., A.M.C., P.H.H., A.M.H., J.M.B., M.L.J., and S.E.M. are co-inventors on US Patent 10,799,523 and US patent applications US 2016/0237427, US 2018/0161356 and US 2019/0383797; and PCT patent application 2016/126995. P.H.H., R.E.O., A.M.H., and M.L.J. are co-inventors on US patent application US 2018/0023081.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

