Bilateral Dysfunction of Otolith Pathway in Patients With Unilateral Idiopathic BPPV Detected by ACS-VEMPs
- PMID: 36090849
- PMCID: PMC9462380
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.921133
Bilateral Dysfunction of Otolith Pathway in Patients With Unilateral Idiopathic BPPV Detected by ACS-VEMPs
Abstract
Objective: To observe the functional status of the otolith pathway in patients with unilateral idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) by combining air-conducted sound elicited cervical vestibular-evoked myogenic potential (ACS-cVEMP) and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potential (ACS-oVEMP).
Methods: One hundred and eighty patients with BPPV were recruited for conventional cVEMP and oVEMP tests. The abnormal rates of VEMPs were compared between BPPV patients and control participants.
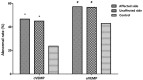
Results: The abnormal rates of cVEMP and oVEMP in BPPV patients were 46.7% (84/180) and 57.2% (103/180) in affected ears, respectively, and 45.0% (81/180) and 56.7% (102/180) in unaffected ears, respectively; both were significantly higher than the abnormal rates of cVEMP and oVEMP in normal control ears. Compared with normal subjects, the cVEMP response rate was lower in affected and unaffected ears in BPPV patients. The abnormal rates of cVEMP and oVEMP were 48.1% (76/158) and 57.6% (91/158) in patients with posterior semicircular canal BPPV, and 36.4% (8/22) and 54.5% (12/22) in lateral semicircular canal BPPV. There was no significant difference in VEMP abnormalities between posterior semicircular canal BPPV and lateral semicircular canal BPPV.
Conclusion: The prevalence of abnormal cVEMPs and oVEMPs in both affected and unaffected ears of patients with BPPV was significantly higher than that observed in the control group. The pathological mechanism of unilateral idiopathic BPPV may be associated with bilateral degeneration of otolith pathways.
Keywords: air-conducted sound; benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; cervical vestibular-evoked myogenic potential; ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potential; vestibular function.
Copyright © 2022 Niu, Han, Duan, Chen, Hu, Chen, Xu, Ren and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of cervical and ocular vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in evaluation of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Sep;273(9):2523-32. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3867-3. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26718546
-
The functional status of vestibular otolith and conductive pathway in patients with unilateral idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Front Neurol. 2023 Jul 20;14:1237516. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1237516. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37545733 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent otolith dysfunction even after successful repositioning in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.J Neurol Sci. 2015 Nov 15;358(1-2):287-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.09.012. Epub 2015 Sep 5. J Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26371697
-
Clinical significance of cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a meta-analysis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Dec;276(12):3257-3265. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05674-4. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31605189 Review.
-
Ocular vs. Cervical Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2020 Oct 26;11:596454. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.596454. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33193065 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Osteoporosis and Vitamin D3 Deficiency in Patients with Idiopathic Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV).Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Apr 28;59(5):862. doi: 10.3390/medicina59050862. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37241094 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Prognostic Implications of Cervical and Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (cVEMP and oVEMP) in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV): A Prospective Study.Audiol Res. 2023 Sep 12;13(5):700-709. doi: 10.3390/audiolres13050061. Audiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37736942 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

