Systematic Analysis and Identification of Molecular Subtypes of TRP-Related Genes and Prognosis Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36090899
- PMCID: PMC9452946
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5388283
Systematic Analysis and Identification of Molecular Subtypes of TRP-Related Genes and Prognosis Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Transient receptor potential channel (TRP) is a superfamily of nonselective cation channels, which is a member of calcium ion channels with a vital role in different calcium ion signal transduction pathways. TRP channel expression is often changed in the tumor, although the role of TRP proteins in lung cancer is unknown.
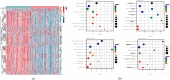
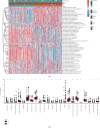
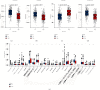
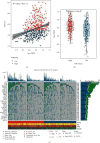
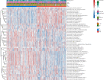
Methods: Molecular Signatures Database (MsigDB) provided the TRP gene set. Univariate Cox regression analysis was performed on The Cancer Genome Atlas Lung Adenocarcinoma (TCGA-LUAD) data collection set employing the coxph function of R package survival to find prognosis-related genes. The R package ConsumusClusterPlus was employed for doing the consistency cluster analysis of TCGA-LUAD samples according to the prognosis-related TRP gene. The R-package limma was utilized for investigating the differential expression of TRP subtypes. According to the differentially expressed genes between subtypes, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was employed to find the major genes and develop the risk model. CIBERPORT algorithm, R package maftools, gene set variation analysis (GSVA), and pRRophetic of R-package were employed for measuring the proportion of immune cells among subtypes, genomic mutation difference, pathway enrichment score, and drug sensitivity analysis.
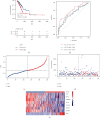
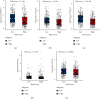
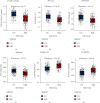
Results: A total of 15 TRP-related genes associated with the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma were found. According to the expression value of 15 genes, lung adenocarcinoma can be sorted into two subcategories. The prognosis of cluster1 is considerably better in comparison with that of cluster2. There were 123 differentially expressed genes between C1 and C2 subtypes, including 6 up- and 117 downregulated genes. There were major variations in the tumor microenvironment between C1 and C2 subtypes. The proportion of CD8 T cells in the C1 subtype was considerably enhanced in comparison with that in the C2 subtype. We further discovered 123 differentially expressed genes among subtypes, and 8 key genes were obtained at the end. The risk score (RS) model developed by the 8-gene signature had good strength in the TCGA validation set, overall set, and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) external dataset. There were major variations in immune checkpoint gene expression, patient sensitivity to immunotherapeutic drugs, immune infiltration, and genomic mutations between high and low groups on the basis of RS.
Conclusions: The risk model developed on the basis of TRP-related genes can help in predicting the prognosis of patients suffering from lung adenocarcinoma and guide immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Yang Guo and Ning Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

