Inactivated tick-borne encephalitis vaccine elicits several overlapping waves of T cell response
- PMID: 36091004
- PMCID: PMC9449805
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.970285
Inactivated tick-borne encephalitis vaccine elicits several overlapping waves of T cell response
Abstract
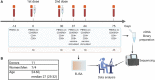
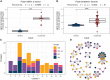
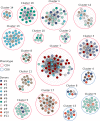
The development and implementation of vaccines have been growing exponentially, remaining one of the major successes of healthcare over the last century. Nowadays, active regular immunizations prevent epidemics of many viral diseases, including tick-borne encephalitis (TBE). Along with the generation of virus-specific antibodies, a highly effective vaccine should induce T cell responses providing long-term immune defense. In this study, we performed longitudinal high-throughput T cell receptor (TCR) sequencing to characterize changes in individual T cell repertoires of 11 donors immunized with an inactivated TBE vaccine. After two-step immunization, we found significant clonal expansion of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, ranging from 302 to 1706 vaccine-associated TCRβ clonotypes in different donors. We detected several waves of T cell clonal expansion generated by distinct groups of vaccine-responding clones. Both CD4+ and CD8+ vaccine-responding T cell clones formed 17 motifs in TCRβ sequences shared by donors with identical HLA alleles. Our results indicate that TBE vaccination leads to a robust T cell response due to the production of a variety of T cell clones with a memory phenotype, which recognize a large set of epitopes.
Keywords: T cell immune response; TBE vaccination; TCR motif; TCR repertoire; clonal expansion; immunological memory; tick-borne encephalitis.
Copyright © 2022 Sycheva, Komech, Pogorelyy, Minervina, Urazbakhtin, Salnikova, Vorovitch, Kopantzev, Zvyagin, Komkov, Mamedov and Lebedev.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Choi KH. Viral polymerases. In: Rossmann MG, Rao VB, editors. Viral molecular machines. Boston: MA: Springer US; (2012). p. 267–304. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0980-9_12 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

