Serum peptidome profiles immune response of COVID-19 Vaccine administration
- PMID: 36091008
- PMCID: PMC9450691
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.956369
Serum peptidome profiles immune response of COVID-19 Vaccine administration
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused significant loss of life and property. In response to the serious pandemic, recently developed vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 have been administrated to the public. Nevertheless, the research on human immunization response against COVID-19 vaccines is insufficient. Although much information associated with vaccine efficacy, safety and immunogenicity has been reported by pharmaceutical companies based on laboratory studies and clinical trials, vaccine evaluation needs to be extended further to better understand the effect of COVID-19 vaccines on human beings.
Methods: We performed a comparative peptidome analysis on serum samples from 95 participants collected at four time points before and after receiving CoronaVac. The collected serum samples were analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) to profile the serum peptides, and also subjected to humoral and cellular immune response analyses to obtain typical immunogenicity information.
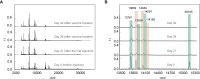
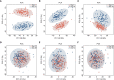
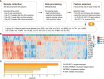
Results: Significant difference in serum peptidome profiles by MALDI-TOF MS was observed after vaccination. By supervised statistical analysis, a total of 13 serum MALDI-TOF MS feature peaks were obtained on day 28 and day 42 of vaccination. The feature peaks were identified as component C1q receptor, CD59 glycoprotein, mannose-binding protein C, platelet basic protein, CD99 antigen, Leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein, integral membrane protein 2B, platelet factor 4 and hemoglobin subunits. Combining with immunogenicity analysis, the study provided evidence for the humoral and cellular immune responses activated by CoronaVac. Furthermore, we found that it is possible to distinguish neutralizing antibody (NAbs)-positive from NAbs-negative individuals after complete vaccination using the serum peptidome profiles by MALDI-TOF MS together with machine learning methods, including random forest (RF), partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), linear support vector machine (SVM) and logistic regression (LR).
Conclusions: The study shows the promise of MALDI-TOF MS-based serum peptidome analysis for the assessment of immune responses activated by COVID-19 vaccination, and discovered a panel of serum peptides biomarkers for COVID-19 vaccination and for NAbs generation. The method developed in this study can help not only in the development of new vaccines, but also in the post-marketing evaluation of developed vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; MALDI-TOF; immune response; peptidome; serum; vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Li, Xu, Xu, Lyu, Liu, Li, Zhang, Sun, Ma, Qiao and Liao.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors BX, QL and QM were employed by Bioyong Technologics, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses Induced by Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines in a Real-World Setting.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:802858. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.802858. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003131 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Detection of COVID-19 Using MALDI-TOF-Based Serum Peptidome Profiling.Anal Chem. 2021 Mar 23;93(11):4782-4787. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04590. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Anal Chem. 2021. PMID: 33656857
-
Safety and immunogenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 ARCoV mRNA vaccine in Chinese adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial.Lancet Microbe. 2022 Mar;3(3):e193-e202. doi: 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00280-9. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Lancet Microbe. 2022. PMID: 35098177 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insights into COVID-19 Vaccine Development Based on Immunogenic Structural Proteins of SARS-CoV-2, Host Immune Responses, and Herd Immunity.Cells. 2021 Oct 29;10(11):2949. doi: 10.3390/cells10112949. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MALDI-TOF mass spectrometric view of the plasma proteome and peptidome.Clin Chem. 2006 Jul;52(7):1223-37. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.069252. Epub 2006 Apr 27. Clin Chem. 2006. PMID: 16644871 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Serum/Plasma Proteomics on SARS-CoV-2 Diagnosis and Prognosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8633. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168633. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in mass spectrometry-based urinary proteomics.Clin Proteomics. 2024 Feb 22;21(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12014-024-09462-z. Clin Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38389064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimal time for COVID-19 vaccination in rituximab-treated dermatologic patients.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 15;14:1138765. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1138765. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006291 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term dysregulation of plasma peptidome in mild and multiple COVID-19 recovered patients revealed by a novel efficient peptidomics workflow.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Feb;417(4):733-746. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05684-0. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39644382
References
-
- Ritchie H, Mathieu E, Rodés-Guirao L, Appel C, Giattino C, Ortiz-Ospina E, et al. . “Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19)”. (2020) Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Retrieved from: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus [Online Resource]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

