Multi-omics analysis reveals the metabolic regulators of duodenal low-grade inflammation in a functional dyspepsia model
- PMID: 36091013
- PMCID: PMC9453867
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.944591
Multi-omics analysis reveals the metabolic regulators of duodenal low-grade inflammation in a functional dyspepsia model
Abstract
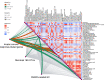
Several gastrointestinal phenotypes and impairment of duodenal mucosal barrier have been reported in clinical studies in patients with functional dyspepsia (FD). Due to the preferential colonization of the mucosa, intestinal microbes and their metabolites are commonly involved in host metabolism and immune responses. However, there are no studies on the intertwined correlation among multi-level data. For more comprehensive illustrating, a multi-omics analysis focusing on the duodenum was performed in the FD rat model. We found that differential microbiomes in the duodenum were significantly correlated with the biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan. The innate immune response-related genes, which were upregulated in the duodenum, were associated with the TLR2/TLR4-NFκB signaling pathway. More importantly, arachidonyl ethanolamide (anandamide, AEA) and endocannabinoid analogues showed linear relationships with the FD phenotypes. Taken together, multi-level data from microbiome, transcriptome and metabolome reveal that AEA may regulate duodenal low-grade inflammation in FD. These results suggest an important cue of gut microbiome-endocannabinoid system axis in the pathogenesis of FD.
Keywords: endocannabinoid; functional dyspepsia; inflammation; innate immune; multi-omics.
Copyright © 2022 Ji, You, Peng, Zhong, Kuang, Li, Du, Chen, Sun, Dai, Huang, Wu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Nojkov B, Zhou S-Y, Dolan RD, Davis EM, Appelman HD, Guo X, et al. Evidence of duodenal epithelial barrier impairment and increased pyroptosis in patients with functional dyspepsia on confocal laser endomicroscopy and "Ex vivo" mucosa analysis. Am J Gastroenterol (2020) 115(11):1891–901. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000827 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

