Combination strategies to optimize the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in haematological malignancies
- PMID: 36091028
- PMCID: PMC9460961
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.954235
Combination strategies to optimize the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in haematological malignancies
Abstract
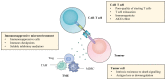
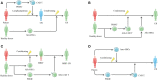
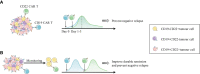
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has revolutionized the therapeutic landscape of haematological malignancies. However, resistance and relapse remain prominent limitations, and they are related to the limited persistence and efficacy of CAR T cells, downregulation or loss of tumour antigens, intrinsic resistance of tumours to death signalling, and immune suppressive microenvironment. Rational combined modality treatments are regarded as a promising strategy to further unlock the antitumor potential of CAR T cell therapy, which can be applied before CAR T cell infusion as a conditioning regimen or in ex vivo culture settings as well as concomitant with or after CAR T cell infusion. In this review, we summarize the combinatorial strategies, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, haematopoietic stem cell transplantation, targeted therapies and other immunotherapies, in an effort to further enhance the effectiveness of this impressive therapy and benefit more patients.
Keywords: CAR T cell; chemotherapy; combination therapy; haematological stem cell transplantation; radiotherapy; relapse; resistance; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Xiao, Wang, Zou, Yang, Wang, Xin, Tu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pasquini MC, Locke FL, Herrera AF, Siddiqi T, Ghobadi A, Komanduri KV, et al. Post-marketing use outcomes of an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, axicabtagene ciloleucel (Axi-cel), for the treatment of Large b cell lymphoma (LBCL) in the united states (US). Blood (2019) 134(Supplement 1):764. doi: 10.1182/Blood-2019-124750 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

