Passive immunization with equine RBD-specific Fab protects K18-hACE2-mice against Alpha or Beta variants of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36091051
- PMCID: PMC9450042
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.948431
Passive immunization with equine RBD-specific Fab protects K18-hACE2-mice against Alpha or Beta variants of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
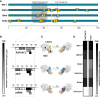
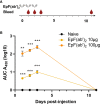
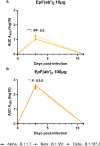
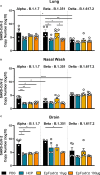
Emergence of variants of concern (VOC) during the COVID-19 pandemic has contributed to the decreased efficacy of therapeutic monoclonal antibody treatments for severe cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, the cost of creating these therapeutic treatments is high, making their implementation in low- to middle-income countries devastated by the pandemic very difficult. Here, we explored the use of polyclonal EpF(ab')2 antibodies generated through the immunization of horses with SARS-CoV-2 WA-1 RBD conjugated to HBsAg nanoparticles as a low-cost therapeutic treatment for severe cases of disease. We determined that the equine EpF(ab')2 bind RBD and neutralize ACE2 receptor binding by virus for all VOC strains tested except Omicron. Despite its relatively quick clearance from peripheral circulation, a 100μg dose of EpF(ab')2 was able to fully protect mice against severe disease phenotypes following intranasal SARS-CoV-2 challenge with Alpha and Beta variants. EpF(ab')2 administration increased survival while subsequently lowering disease scores and viral RNA burden in disease-relevant tissues. No significant improvement in survival outcomes or disease scores was observed in EpF(ab')2-treated mice challenged using the Delta variant at 10μg or 100µg doses. Overall, the data presented here provide a proof of concept for the use of EpF(ab')2 in the prevention of severe SARS-CoV-2 infections and underscore the need for either variant-specific treatments or variant-independent therapeutics for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; EpF(ab’)2; Equine F(ab’)2; K18-hACE2 transgenic mice; SARS-CoV-2; passive immunization; polyclonal antibodies; variant of concern (VOC).
Copyright © 2022 Barbier, Lee, Vikharankar, Rajpathak, Kadam, Wong, Russ, Cyphert, Miller, Rader, Cooper, Kang, Sen-Kilic, Wong, Winters, Bevere, Martinez, Devarumath, Shaligram and Damron.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors MV, SR and US were employed by company Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd. Author NK was employed by company Isera Biological Pvt. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluating Antibody Mediated Protection against Alpha, Beta, and Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern in K18-hACE2 Transgenic Mice.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0218421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02184-21. Epub 2022 Jan 26. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35080423 Free PMC article.
-
RBD-VLP Vaccines Adjuvanted with Alum or SWE Protect K18-hACE2 Mice against SARS-CoV-2 VOC Challenge.mSphere. 2022 Aug 31;7(4):e0024322. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00243-22. Epub 2022 Aug 15. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 35968964 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic equine hyperimmune antibodies with high and broad-spectrum neutralizing activity protect rodents against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 17;14:1066730. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1066730. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36875106 Free PMC article.
-
K18- and CAG-hACE2 Transgenic Mouse Models and SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Neurodegeneration Research.Molecules. 2022 Jun 28;27(13):4142. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134142. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19: Challenges of Viral Variants.Annu Rev Med. 2023 Jan 27;74:31-53. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-042921-020956. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Annu Rev Med. 2023. PMID: 35850493 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutralization of Different Variants of SARS-CoV-2 by a F(ab')2 Preparation from Sera of Horses Immunized with the Viral Receptor Binding Domain.Antibodies (Basel). 2023 Dec 7;12(4):80. doi: 10.3390/antib12040080. Antibodies (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38131802 Free PMC article.
-
Equine Polyclonal Antibodies Prevent Acute Chikungunya Virus Infection in Mice.Viruses. 2023 Jun 29;15(7):1479. doi: 10.3390/v15071479. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515166 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza virus strains expressing SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain protein confer immunity in K18-hACE2 mice.Vaccine X. 2024 Aug 3;20:100543. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2024.100543. eCollection 2024 Oct. Vaccine X. 2024. PMID: 39221180 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-modified measles vaccines encoding oligomeric, prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoproteins boost neutralizing antibody responses to Omicron and historical variants, independent of measles seropositivity.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0292823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02928-23. Epub 2024 Jan 9. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38193729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piccoli L, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Czudnochowski N, Walls AC, Beltramello M, et al. . Mapping neutralizing and immunodominant sites on the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain by structure-guided high-resolution serology. Cell (2020) 183(4):1024. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.037 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

