Anti-proliferative effect and underlying mechanism of ethoxy-substituted phylloquinone (vitamin K1 derivative) from Spinacia oleracea leaf and enhancement of its extractability using radiation technology
- PMID: 36091087
- PMCID: PMC9452621
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-022-03264-6
Anti-proliferative effect and underlying mechanism of ethoxy-substituted phylloquinone (vitamin K1 derivative) from Spinacia oleracea leaf and enhancement of its extractability using radiation technology
Abstract
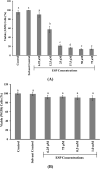
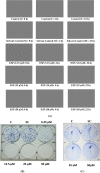
In our previous studies, a novel antimutagenic compound, 2-ethoxy-3-(3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-ethyl) naphthaquinone-1,4-dione (ethoxy-substituted phylloquinone; ESP) from spinach was characterized and mechanism contributing to its antimutagenicity was deduced. In the current study, anti-proliferative activity of ESP was assessed in lung cancer (A549) cells using MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazole-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide], clonogenic assays and cell cycle analysis. ESP treatment showed selective cytotoxicity against lung cancer cells and no cytotoxicity in normal lung (WI38) cells. Cell cycle analysis revealed that ESP treatment arrests A549 cell population in G2-M phase. In-silico analysis indicated positive drug-likeness features of ESP. Molecular docking showed H-bonding and hydrophobic interactions between ESP and B-DNA dodecamer residues at minor groove. SWATH-MS (Sequential Window Acquisition of All Theoretical Mass Spectra) based proteomic analysis indicated down-regulation of proteins involved in EGFR signaling, NEDDylation and other metabolic pathways and up-regulation of tumor suppressor (STAT1 and NDRG1) proteins. Treatment of spinach powder with gamma radiation (5-20 kGy) from cobalt (Co-60) enhanced the extractability of ESP up to 4.4-fold at the highest dose of 20 kGy. Scanning electron microscopy of spinach powder displayed decrease in smoothness and compactness with increase in radiation dose attributing to its enhanced extractability. Increase in the extractability of ESP with increasing radiation doses as measured by fluorescence intensity and dry weight basis was strongly correlated. Nonetheless, radiation treatment did not affect the functionality of ESP in terms of anti-proliferative and antimutagenic activities. Current findings thus highlight broad spectrum bioactivity of ESP from spinach, its underlying mechanism and applicability of radiation technology in enhancing extractability.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-022-03264-6.
Keywords: Lung cancer cell; Minor groove binding; Molecular docking; Radiation technology; SWATH-MS.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAuthors declare no conflict of interest with respect to the study described in the manuscript.
Figures

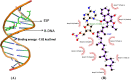
 H-bond;
H-bond;  Hydrophobic interactions
Hydrophobic interactions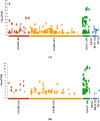
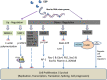
 Normal Pathway (in absence of ESP);
Normal Pathway (in absence of ESP);  Inhibition (in presence of ESP)
Inhibition (in presence of ESP)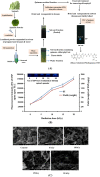

Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanism of antimutagenicity by an ethoxy-substituted phylloquinone (vitamin K1 derivative) from spinach (Spinacea oleracea L.).Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Oct 1;330:109216. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109216. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 32810488
-
Purification and Characterization of the Principal Antimutagenic Bioactive as Ethoxy-Substituted Phylloquinone from Spinach (Spinacea oleracea L.) Based on Evaluation in Models Including Human Lymphoblast TK+/- Cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2016 Nov 23;64(46):8773-8782. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03915. Epub 2016 Nov 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 27806562
-
gamma-Irradiation dose: effects on baby-leaf spinach ascorbic acid, carotenoids, folate, alpha-tocopherol, and phylloquinone concentrations.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Apr 28;58(8):4901-6. doi: 10.1021/jf100146m. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20329797
-
Bellidifolin Inhibits Proliferation of A549 Cells by Regulating STAT3/COX-2 Expression and Protein Activity.J Oncol. 2020 Nov 21;2020:1723791. doi: 10.1155/2020/1723791. eCollection 2020. J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33299414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis of vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) by plant peroxisomes and its integration into signaling molecule synthesis pathways.Subcell Biochem. 2013;69:213-29. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-6889-5_12. Subcell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23821151 Review.
References
-
- Chemat F, Rombaut N, Sicaire AG, Meullemiestre A, Fabiano-Tixier AS, Abert-Vian M. Ultrasound assisted extraction of food and natural products. mechanisms, techniques, combinations, protocols and applications. A Review Ultrason Sonochem. 2017;34:540–560. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.06.035. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

