Bionic research on Paramisgurnus dabryanus scales for drag reduction
- PMID: 36091191
- PMCID: PMC9367982
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra04073e
Bionic research on Paramisgurnus dabryanus scales for drag reduction
Abstract
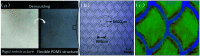
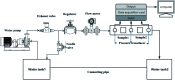
Drag reduction is a key problem in marine vehicles and fluid transportation industries. Reducing drag strategies and mechanisms need to be further investigated. To explore a bionic approach for reducing flow resistance, experimental and numerical simulation research was conducted to study the drag reduction characteristics of the Paramisgurnus dabryanus surface microstructure. In this study, the large-area flexible surface of the bionic loach scale was prepared by the template method of one-step demoulding. The water tunnel experiment results show that compared with the smooth surface, the drag reduction rate of the bionic surface ranges from 9.42% to 17.25%. And the numerical simulation results indicate that the pressure gradient and low-speed vortex effect created by the bionic loach scales can effectively reduce the friction drag. The results of experimental data and numerical simulation both prove that the bionic scales of Paramisgurnus dabryanus can achieve the underwater drag reduction function. This research provides a reference for drag reduction in marine industries and fluid delivery applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Drag reduction mechanism of Paramisgurnus dabryanus loach with self-lubricating and flexible micro-morphology.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 30;10(1):12873. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69801-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32732993 Free PMC article.
-
A bio-inspired two-stage bionic drag reduction method.Rev Sci Instrum. 2024 Mar 1;95(3):035118. doi: 10.1063/5.0196338. Rev Sci Instrum. 2024. PMID: 38497834
-
Drag reduction using bionic groove surface for underwater vehicles.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 25;11:1223691. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1223691. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37691898 Free PMC article.
-
Thriving artificial underwater drag-reduction materials inspired from aquatic animals: progresses and challenges.RSC Adv. 2021 Jan 18;11(6):3399-3428. doi: 10.1039/d0ra08672j. eCollection 2021 Jan 14. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35424313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Damage of polyethylene microplastics on the intestine multilayer barrier, blood cell immune function and the repair effect of Leuconostoc mesenteroides DH in the large-scale loach (Paramisgurnus dabryanus).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Apr;147:109460. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109460. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38382690 Review.
Cited by
-
Bidirectional Underwater Drag Reduction on Bionic Flounder Two-Tier Structural Surfaces.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Mar 11;8(1):116. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8010116. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36975346 Free PMC article.
-
Design and experiment of a bionic drag-reducing digger for tuberous crops under heavy soil conditions.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 25;20(2):e0318526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0318526. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39999094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sindagi S. Vijayakumar R. Ships Offshore Struct. 2020;16:968–979. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2020.1790296. - DOI
-
- Wu T. Chen W. Zhao A. He P. Chen H. Ocean Eng. 2020;218:107902. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107902. - DOI
-
- Kumagai I. Takahashi Y. Murai Y. Ocean Eng. 2015;95:183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2014.11.019. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

