A Naive Bayes model on lung adenocarcinoma projection based on tumor microenvironment and weighted gene co-expression network analysis
- PMID: 36091346
- PMCID: PMC9403296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idm.2022.07.009
A Naive Bayes model on lung adenocarcinoma projection based on tumor microenvironment and weighted gene co-expression network analysis
Abstract
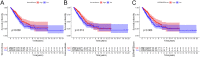
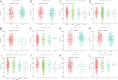
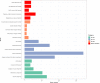
Based on the lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) gene expression data from the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) database, the Stromal score, Immune score and Estimate score in tumor microenvironment (TME) were computed by the Estimation of Stromal and Immune cells in Malignant Tumor tissues using Expression data (ESTIMATE) algorithm. And gene modules significantly related to the three scores were identified by weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Based on the correlation coefficients and P values, 899 key genes affecting tumor microenvironment were obtained by selecting the two most correlated modules. It was suggested through Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis that these key genes were significantly involved in immune-related or cancer-related terms. Through univariate cox regression and elastic network analysis, genes associated with prognosis of the LUAD patients were screened out and their prognostic values were further verified by the survival analysis and the University of ALabama at Birmingham CANcer (UALCAN) database. The results indicated that eight genes were significantly related to the overall survival of LUAD. Among them, six genes were found differentially expressed between tumor and control samples. And immune infiltration analysis further verified that all the six genes were significantly related to tumor purity and immune cells. Therefore, these genes were used eventually for constructing a Naive Bayes projection model of LUAD. The model was verified by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve where the area under curve (AUC) reached 92.03%, which suggested that the model could discriminate the tumor samples from the normal accurately. Our study provided an effective model for LUAD projection which improved the clinical diagnosis and cure of LUAD. The result also confirmed that the six genes in the model construction could be the potential prognostic biomarkers of LUAD.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma; Naive Bayes model; Prognostic biomarkers; Tumor microenvironment; Weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The prognostic value of immune escape-related genes in lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):2647-2661. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2295. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988926 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment related novel signature predict lung adenocarcinoma survival.PeerJ. 2021 Jan 14;9:e10628. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10628. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33520448 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a Prognostic Immune-Related LncRNA Risk Model for Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 18;9:648806. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.648806. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869203 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic model of lung adenocarcinoma based on immunoprognosis-related genes and related drug prediction.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Sep 30;16(9):5860-5877. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-569. Epub 2024 Sep 26. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 39444861 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis to identify a novel diagnostic marker of lung adenocarcinoma and its immune infiltration landscape.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 20;13:1199608. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1199608. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37409245 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Construction and validation of prognostic models for acute kidney disease and mortality in patients at risk of malnutrition: an interpretable machine learning approach.Clin Kidney J. 2025 Mar 13;18(4):sfaf080. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaf080. eCollection 2025 Apr. Clin Kidney J. 2025. PMID: 40236512 Free PMC article.
-
A Machine Learning Model for the Prediction of COVID-19 Severity Using RNA-Seq, Clinical, and Co-Morbidity Data.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 18;14(12):1284. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14121284. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38928699 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

