Differential microRNA profiles of intramuscular and secreted extracellular vesicles in human tissue-engineered muscle
- PMID: 36091396
- PMCID: PMC9452896
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.937899
Differential microRNA profiles of intramuscular and secreted extracellular vesicles in human tissue-engineered muscle
Abstract
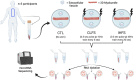
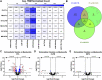
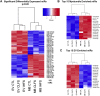
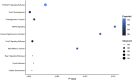
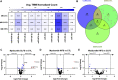
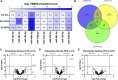
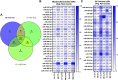
Exercise affects the expression of microRNAs (miR/s) and muscle-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). To evaluate sarcoplasmic and secreted miR expression in human skeletal muscle in response to exercise-mimetic contractile activity, we utilized a three-dimensional tissue-engineered model of human skeletal muscle ("myobundles"). Myobundles were subjected to three culture conditions: no electrical stimulation (CTL), chronic low frequency stimulation (CLFS), or intermittent high frequency stimulation (IHFS) for 7 days. RNA was isolated from myobundles and from extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by myobundles into culture media; miR abundance was analyzed by miRNA-sequencing. We used edgeR and a within-sample design to evaluate differential miR expression and Pearson correlation to evaluate correlations between myobundle and EV populations within treatments with statistical significance set at p < 0.05. Numerous miRs were differentially expressed between myobundles and EVs; 116 miRs were differentially expressed within CTL, 3 within CLFS, and 2 within IHFS. Additionally, 25 miRs were significantly correlated (18 in CTL, 5 in CLFS, 2 in IHFS) between myobundles and EVs. Electrical stimulation resulted in differential expression of 8 miRs in myobundles and only 1 miR in EVs. Several KEGG pathways, known to play a role in regulation of skeletal muscle, were enriched, with differentially overrepresented miRs between myobundle and EV populations identified using miEAA. Together, these results demonstrate that in vitro exercise-mimetic contractile activity of human engineered muscle affects both their expression of miRs and number of secreted EVs. These results also identify novel miRs of interest for future studies of the role of exercise in organ-organ interactions in vivo.
Keywords: engineered tissue; extracellular vescicles; miRNA sequencing; microRNA; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2022 Vann, Zhang, Khodabukus, Orenduff, Chen, Corcoran, Truskey, Bursac and Kraus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cell Density and Joint microRNA-133a and microRNA-696 Inhibition Enhance Differentiation and Contractile Function of Engineered Human Skeletal Muscle Tissues.Tissue Eng Part A. 2016 Apr;22(7-8):573-83. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2015.0359. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016. PMID: 26891613 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct microRNA and protein profiles of extracellular vesicles secreted from myotubes from morbidly obese donors with type 2 diabetes in response to electrical pulse stimulation.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1143966. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1143966. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37064893 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Stimulation of α- and β-Adrenoceptors in Mice Differentially Alters Small RNA Content of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles.Cells. 2021 May 15;10(5):1211. doi: 10.3390/cells10051211. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34063503 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation enhances the ability of serum extracellular vesicles to regenerate aged skeletal muscle after injury.Exp Gerontol. 2023 Jun 15;177:112179. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112179. Epub 2023 May 1. Exp Gerontol. 2023. PMID: 37087025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Skeletal Muscle Physiology and Sarcopenia: The Importance of Physical Exercise and Nutrition.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 13;16(18):3097. doi: 10.3390/nu16183097. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma extracellular vesicles carry immune system-related peptides that predict human longevity.Geroscience. 2025 Apr;47(2):1455-1469. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01454-z. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39695065 Free PMC article.
-
Human Myobundle Platform for Studying the Role of Notch Signaling in Satellite Cell Phenotype and Function.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 May;14(12):e2404695. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202404695. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 40123310
-
Immune System-Related Plasma Pathogenic Extracellular Vesicle Subpopulations Predict Osteoarthritis Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 21;25(23):12504. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312504. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684216 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential of in vitro extracellular vesicle generation in reproductive biology.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Sep 5;3(9):e70007. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70007. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39238549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy on Fat Mass and Glucose Homeostasis in Humans and Animals: A Narrative Review with Systematic Literature Search.Sports Med. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s40279-025-02263-w. Online ahead of print. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40576707 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

