The effects of health insurance and physical exercise participation on life satisfaction of older people in China-Based on CHNS panel data from 2006 to 2015
- PMID: 36091561
- PMCID: PMC9458912
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.858191
The effects of health insurance and physical exercise participation on life satisfaction of older people in China-Based on CHNS panel data from 2006 to 2015
Abstract
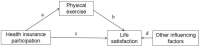
Background: In China, the problem of aging population has become more and more serious. The factors influencing life satisfaction of older people are becoming a significant issue. This study explores the effects of health insurance and physical exercise on life satisfaction of older people in China.
Method: This study used an unbalanced panel dataset (n = 6,393, T = 4) of older adults aged 60-80 years from the 2006 to 2015 China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). A panel ordered logistic regression model was developed to examine the effects of health insurance and physical exercise on older people' life satisfaction. Mediation tests were used to examine the mediating role of physical exercise in the effect of health insurance on life satisfaction of older people.
Result: Life satisfaction of older people was positively associated with participation in health insurance (OR = 1.439) and physical exercise (OR = 1.033). Participation in government health insurance, urban employee health insurance (UEBMI), new rural cooperative health insurance (NRCMI), and other commercial health insurance all have positive effects on life satisfaction of older people. Physical exercise plays a masking role in the effect of health insurance on life satisfaction of older people.
Conclusion: Participation in health insurance and physical exercise are important means to promote life satisfaction among older people. Physical exercise affects the impact of health insurance on older people's life satisfaction.
Keywords: CHNS; active aging; health insurance; older people; physical exercise.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Zeng and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Easterlin RA, Wang F, Wang S. Growth and happiness in China, 1990–2015. In: A modern guide to the economics of happiness. Edward Elgar Publishing; (2021). p. 129–161. 10.4337/9781788978767.00017 - DOI
-
- Han Y, Fu JP. Policy supply of elderly care services in China: evolution, governance framework, and future directions. Lanzhou Acad J. (2020) 9:187–98.
-
- Pei CH. The new goal of building a new system of a higher-level open economy - a little experience from studying ”The CPC Central Committee's Suggestions on Formulating the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-term Goals for 2035“. Res Ref. (2020) 24:89–93. 10.16110/j.cnki.issn2095-3151.2020.24.009 - DOI
-
- Walker A. A strategy for active ageing. Int Soc Secur Rev. (2002) 55:121–39. 10.1111/1468-246X.00118 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical