Hotspots and trends in ophthalmology in recent 5 years: Bibliometric analysis in 2017-2021
- PMID: 36091704
- PMCID: PMC9462464
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.988133
Hotspots and trends in ophthalmology in recent 5 years: Bibliometric analysis in 2017-2021
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the hotspots and research trends of ophthalmology research.
Method: Ophthalmology research literature published between 2017 and 2021 was obtained in the Web of Science Core Collection database. The bibliometric analysis and network visualization were performed with the VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Publication-related information, including publication volume, citation counts, countries, journals, keywords, subject categories, and publication time, was analyzed.
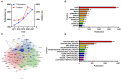
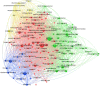
Results: A total of 10,469 included ophthalmology publications had been cited a total of 7,995 times during the past 5 years. The top countries and journals for the number of publications were the United States and the Ophthalmology. The top 25 global high-impact documents had been identified using the citation ranking. Keyword co-occurrence analysis showed that the hotspots in ophthalmology research were epidemiological characteristics and treatment modalities of ocular diseases, artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology, COVID-19-related telemedicine, and screening and prevention of ocular diseases. Keyword burst analysis revealed that "neural network," "pharmacokinetics," "geographic atrophy," "implementation," "variability," "adverse events," "automated detection," and "retinal images" were the research trends of research in the field of ophthalmology through 2021. The analysis of the subject categories demonstrated the close cooperation relationships that existed between different subject categories, and collaborations with non-ophthalmology-related subject categories were increasing over time in the field of ophthalmology research.
Conclusions: The hotspots in ophthalmology research were epidemiology, prevention, screening, and treatment of ocular diseases, as well as artificial intelligence and fundus imaging technology and telemedicine. Research trends in ophthalmology research were artificial intelligence, drug development, and fundus diseases. Knowledge from non-ophthalmology fields is likely to be more involved in ophthalmology research.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; hotspots; literature; ophthalmology; research trend.
Copyright © 2022 Tan, Zhu, Zou, Zhang, Yu, Li, Jin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comprehensive bibliometric research in neuroscience: focusing on ophthalmology.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 15;17:1106023. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1106023. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37397445 Free PMC article.
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
Global trends and performances in diabetic retinopathy studies: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 13;11:1128008. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1128008. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37124794 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends and hotspots on septic shock: a bibliometric study and visualization analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 27;11:1490462. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1490462. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39664313 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Trends and Hotspots in Hip Arthroplasty: A Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization Study of Last Five-Year Publications.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2023;11(8):493-501. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2023.70790.3313. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2023. PMID: 37674701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive bibliometric research in neuroscience: focusing on ophthalmology.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jun 15;17:1106023. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1106023. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37397445 Free PMC article.
-
Highly cited publication performance in the ophthalmology category in the Web of Science database: a bibliometric analysis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Jul 18;16(7):1155-1163. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.07.22. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37465509 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric analysis of the uveitis literature and research trends over the past two decades.BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023 Sep;8(1):e001330. doi: 10.1136/bmjophth-2023-001330. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37714667 Free PMC article.
-
Turkish Retinoblastoma Research: A Bibliometric Analysis (1966-2024).Turk J Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 25;54(5):282-290. doi: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2024.43247. Turk J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39463168 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in ophthalmology: a bibliometric analysis of the 5-year trends in literature.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 1;12:1580583. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1580583. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40665980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Report on Vision. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2019).
-
- Taylor-Walker G, Lynn SA, Keeling E, Munday R, Johnston DA, Page A, et al. . The Alzheimer's-related amyloid beta peptide is internalised by R28 neuroretinal cells and disrupts the microtubule associated protein 2 (MAP-2). Exp Eye Res. (2016) 153:110–21. 10.1016/j.exer.2016.10.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

