Exploration of metabolic responses towards hypoxia mimetic DMOG in cancer cells by using untargeted metabolomics
- PMID: 36091722
- PMCID: PMC9460158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103426
Exploration of metabolic responses towards hypoxia mimetic DMOG in cancer cells by using untargeted metabolomics
Abstract
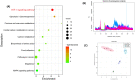
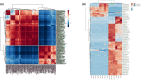
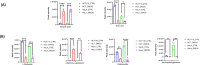
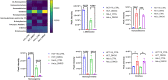
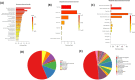
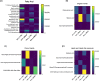
Hypoxia is considered as one of the most crucial elements of tumor microenvironment. The hypoxia inducible transcription factors (HIF-1/2) are used by the cancer cells to adapt hypoxic microenvironment through regulating the expression of various target genes, including metabolic enzymes. Dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG), a hypoxic mimetic used for HIF stabilisation in cell and animal models, also demonstrates multiple metabolic effects. In past, it was shown that in cancer cells, DMOG treatment alters mitochondrial ATP production, glycolysis, respiration etc. However, a global landscape of metabolic level alteration in cancer cells during DMOG treatment is still not established. In the current work, the metabolic landscape of cancer cells during DMOG treatment is explored by using untargeted metabolomics approach. Results showed that DMOG treatment primarily alters the one carbon and lipid metabolism. The levels of one-carbon metabolism related metabolites like serine, ornithine, and homomethionine levels significantly altered during DMOG treatment. Further, DMOG treatment reduces the global fatty acyls like palmitic acids, stearic acids, and arachidonic acid levels in cancer cell lines. Additionally, we found an alteration in glycolytic metabolites known to be regulated by hypoxia in cancer cell lines. Collectively, the results provided novel insights into the metabolic impact of DMOG on cancer cells and showed that the use of DMOG to induce hypoxia yields similar metabolic features relative to physiological hypoxia.
Keywords: Dimethyloxalylglycine (DMOG); Fatty acyls; Hypoxia; Lipidomics; Untargeted Metabolomics.
© 2022 The Author.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Aragonés J., Schneider M., Van Geyte K., Fraisl P., Dresselaers T., Mazzone M., Dirkx R., Zacchigna S., Lemieux H., Jeoung N.H., Lambrechts D., Bishop T., Lafuste P., Diez-Juan A., Harten S.K., Van Noten P., De Bock K., Willam C., Tjwa M., Grosfeld A., Navet R., Moons L., Vandendriessche T., Deroose C., Wijeyekoon B., Nuyts J., Jordan B., Silasi-Mansat R., Lupu F., Dewerchin M., Pugh C., Salmon P., Mortelmans L., Gallez B., Gorus F., Buyse J., Sluse F., Harris R.A., Gnaiger E., Hespel P., Van Hecke P., Schuit F., Van Veldhoven P., Ratcliffe P., Baes M., Maxwell P., Carmeliet P. Deficiency or inhibition of oxygen sensor Phd1 induces hypoxia tolerance by reprogramming basal metabolism. Nat. Genet. 2008;40(2):170–180. - PubMed
-
- Armitage E.G., Barbas C. Metabolomics in cancer biomarker discovery: current trends and future perspectives. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014;87:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

