In-silico investigation of a novel inhibitors against the antibiotic-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria
- PMID: 36091725
- PMCID: PMC9460163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.103424
In-silico investigation of a novel inhibitors against the antibiotic-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria
Abstract
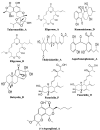
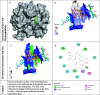
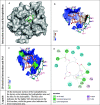
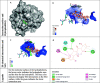
Antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat or prevent bacterial infections. They work by either killing or stopping bacteria from spreading. Nevertheless, it appeared in the last decade, Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are bacteria resistant to antibiotics and cannot be controlled or killed by them. In the presence of an antibiotic, they can live and even reproduce. The Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria is appearing to be a multidrug-resistant pathogen. Many factors contribute to antibiotic resistance, including unfettered access to antimicrobials, incorrect drug selection, misuse, and low-quality antibiotics. Here, we investigated in-silico docking screening and analysis for ten natural marine fungus extracted compounds. The resulted data were examined for the best binding affinity, toxicity, and chemical interactions. The most superior compound was elipyrone A with six hydrogen bonds, -8.5 of binding affinity, and preferable results in the SWISS-ADME examination. It is well known that "Declining corporate investment and a lack of innovation in the development of new antibiotics are weakening efforts to battle drug-resistant illnesses," according to the World Health Organization (WHO). So, we extended our effort to predict a new natural compound to overcome the resistance of this bacteria.
Keywords: Antibiotics; In-silico docking; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Resistant bacteria.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
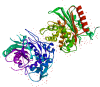


Similar articles
-
Multidrug Resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: Identification of Functionally Important Residues in the MtrD Efflux Protein.mBio. 2019 Nov 19;10(6):e02277-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02277-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31744915 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Inhibitory Peptides Targeting the Neisseria gonorrhoeae MtrCDE Efflux Pump Increase Antibiotic Susceptibility.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jan 18;66(1):e0154221. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01542-21. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34633841 Free PMC article.
-
Future Prospects for Neisseria gonorrhoeae Treatment.Antibiotics (Basel). 2018 Jun 15;7(2):49. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7020049. Antibiotics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29914071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial activity of enacyloxin IIa and gladiolin against the urogenital pathogens Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Ureaplasma spp.J Appl Microbiol. 2021 May;130(5):1546-1551. doi: 10.1111/jam.14858. Epub 2020 Oct 21. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32966677
-
New Antibiotics for Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains: Latest Research Developments and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2021 May 2;26(9):2671. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092671. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34063264 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Synthesis of Novel Antimicrobial Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 22;12(3):628. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030628. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Fluoroquinolones with Possible Antibacterial Activity in Gram-Negative Resistant Pathogens: In Silico Drug Discovery.Molecules. 2023 Oct 4;28(19):6929. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196929. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836772 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling of cyclotides as antimicrobial agents against Neisseria gonorrhoeae PorB porin protein: integration of docking, immune, and molecular dynamics simulations.Front Chem. 2024 Nov 25;12:1493165. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1493165. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39659871 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and Experimental Study of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) as Antimicrobial Agents against Neisseria gonorrhoeae.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Apr 9;17(14):20628-20646. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c15851. Epub 2025 Mar 27. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 40145890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aallaei M., Molaakbari E., Mostafavi P., Salarizadeh N., Maleksah R.E., Afzali D. Investigation of Cu metal nanoparticles with different morphologies to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 main protease and spike glycoprotein using molecular docking and dynamics simulation. J. Mol. Struct. 2022;1253 doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.132301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aliashkevich A., Cava F. LD-transpeptidases: the great unknown among the peptidoglycan cross-linkers. FEBS J. 2021;289(16):4718–4730. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

