Gynostemma pentaphyllum for dyslipidemia: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36091752
- PMCID: PMC9459123
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917521
Gynostemma pentaphyllum for dyslipidemia: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the lipid-lowering effect and safety of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (GP) used alone or as adjunctive therapy for dyslipidemia. Methods: Eight databases and three clinical trial registries were searched until January 2022. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing the effectiveness of GP for dyslipidemia were included. Trial quality was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool 2.0. Data were analyzed by RevMan 5.4 with effects estimated as risk ratio (RR) or mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Results: Twenty-two RCTs involving 2,407 dyslipidemia participants were included. Regarding the risk of bias, 14 RCTs had some concerns, seven RCTs were high, and one trial was low. GP was comparable to n-3 fatty acids (RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.62-1.28) and red yeast rice (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.1-1.12) on normalization of serum lipids. GP plus n-3 fatty acid was superior in normalization of triglycerides (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) than n-3 fatty acids (RR 1.34, 95% CI 1.01-1.77). GP was similar to lipid-lowering agents (statins, fibrates, and n-3 fatty acids) in regulating TG, TC, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). GP plus lipid-lowering agents were superior to lipid-lowering agents in TG (MD -0.65 mmol/L, 95% CI -1.03 to -0.28), LDL-C (MD -0.57 mmol/L, 95% CI -1.07 to -0.08), and HDL-C (MD 0.15 mmol/L, 95% CI 0.11-0.20). GP was inferior to red yeast rice in TC (MD 0.64 mmol/L, 95% CI 0.15-1.13), TG (MD 0.43 mmol/L, 95% CI 0.15-0.71), and HDL-C (MD -0.25 mmol/L, 95% CI -0.47 to -0.04). GP had fewer adverse events than lipid-lowering drugs. Conclusion: Very low certainty evidence showed that GP's effects on TC, TG, and HDL-C were comparable to that of lipid-lowering agents. Low certainty evidence showed that red yeast rice was superior to GP in TC, TG, and HDL-C. Low to moderate certainty evidence showed that the effects of GP plus lipid-lowering agents were superior to that of lipid-lowering agents on TG, LDL-C, and HDL-C. GP use for more than 8 weeks appears safe. Systematic Review Registration: https://inplasy.com/, identifier INPLASY202210135.
Keywords: Safety of Gynostemma pentaphyllum; dyslipidemia; lipid-lowering agents; meta-analysis; randomized controlled trials; red yeast rice extracts; systematic review.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Zhao, Fang, Pu, Kong and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
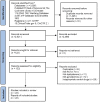

Similar articles
-
Effects of the combination of red yeast rice-containing commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation with statins for dyslipidemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 23;15:1398934. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1398934. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39108747 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety assessment of traditional Chinese patent medicine for dyslipidemia: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024 Jun 30;14(3):419-446. doi: 10.21037/cdt-24-146. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38975001 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of berberine for dyslipidaemias: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Phytomedicine. 2018 Nov 15;50:25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.212. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466986
-
Effectiveness and safety of Hwangryunhaedok-Tang (Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang, Oren-Gedoku-to) for dyslipidemia: A protocol for a PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 18;99(51):e23367. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023367. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33371067 Free PMC article.
-
Vegan dietary pattern for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 25;2(2):CD013501. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013501.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33629376 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory Effects of Heat-Processed Gynostemma pentaphyllum Extract (Actiponin®) and Its Components on Cartilage Breakdown in Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 18;26(4):1728. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041728. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004191 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the combination of red yeast rice-containing commercial Chinese polyherbal preparation with statins for dyslipidemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 23;15:1398934. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1398934. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39108747 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Natural Products in the Management of Cardiovascular Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(8):624-638. doi: 10.2174/0113816128295053240207090928. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38477208 Review.
-
High-Altitude Medicinal Plants as Promising Source of Phytochemical Antioxidants to Combat Lifestyle-Associated Oxidative Stress-Induced Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;17(8):975. doi: 10.3390/ph17080975. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolome combined with gut microbiome revealed the lipid-lowering mechanism of Xuezhiping capsule on hyperlipidemic hamster induced by high fat diet.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 20;10:1147910. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1147910. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36891237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baigent C., Keech A., Kearney P. M., Blackwell L., Buck G., Pollicino C., et al. (2005). Efficacy and safety of cholesterol-lowering treatment: Prospective meta-analysis of data from 90, 056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 366, 1267–1278. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67394-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

