Insights on prospects of nano-siRNA based approaches in treatment of Cancer
- PMID: 36091772
- PMCID: PMC9452808
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.985670
Insights on prospects of nano-siRNA based approaches in treatment of Cancer
Abstract
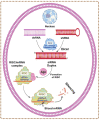
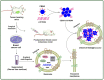
siRNA interference, commonly referred to as gene silence, is a biological mechanism that inhibits gene expression in disorders such as cancer. It may enhance the precision, efficacy, and stability of medicines, especially genetic therapies to some extent. However, obstacles such as the delivery of oligonucleotide drugs to inaccessible areas of the body and the prevalence of severe side effects must be overcome. To maximize their potential, it is thus essential to optimize their distribution to target locations and limit their toxicity to healthy cells. The action of siRNA may be harnessed to delete a similar segment of mRNA that encodes a protein that causes sickness. The absence of an efficient delivery mechanism that shields siRNA from nuclease degradation, delivers it to cancer cells and releases it into the cytoplasm of specific cancer cells without causing side effects is currently the greatest obstacle to the practical implementation of siRNA therapy. This article focuses on combinations of siRNA with chemotherapeutic drug delivery systems for the treatment of cancer and gives an overview of several nanocarrier formulations in both research and clinical applications.
Keywords: cancer; exosomes; gene silencing; nanomaterials; nanoparticles; siRNA.
Copyright © 2022 Goyal, Chopra, singh, Dua and Gautam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent Insights into Nano-mediated siRNA Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Metab. 2025;25(8):554-563. doi: 10.2174/0113892002339055241211050131. Curr Drug Metab. 2025. PMID: 39716803 Review.
-
Efficient nanocarriers of siRNA therapeutics for cancer treatment.Transl Res. 2019 Dec;214:62-91. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31369717 Review.
-
Nanocarrier mediated delivery of siRNA/miRNA in combination with chemotherapeutic agents for cancer therapy: current progress and advances.J Control Release. 2014 Nov 28;194:238-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Sep 7. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25204288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Technology for Clinical Translation of siRNA Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00368. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31397996 Review.
-
Cell-free synthesis of connexin 43-integrated exosome-mimetic nanoparticles for siRNA delivery.Acta Biomater. 2019 Sep 15;96:517-536. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31284098
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology-assisted combination drug delivery: a progressive approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.Ther Deliv. 2024;15(11):893-910. doi: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2394012. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Ther Deliv. 2024. PMID: 39268925 Review.
-
A systematic review of non-coding RNA therapeutics in early clinical trials: a new perspective against cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Aug 5;22(1):731. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05554-4. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39103911 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Cell-Penetrating and Fusogenic TAT-HA2 Peptide Performance in Peptideplex, Multicomponent, and Conjugate siRNA Delivery Systems.ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 20;9(48):47461-47474. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05808. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39651078 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing nanotechnology for cancer treatment.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 20;12:1514890. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1514890. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39902172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biopolymer-Based Nanosystems for siRNA Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors including Breast Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 1;15(1):153. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010153. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alshaer W., Hillaireau H., Vergnaud J., Mura S., Deloménie C., Sauvage F., et al. (2018). Aptamer-guided siRNA-loaded nanomedicines for systemic gene silencing in CD-44 expressing murine triple-negative breast cancer model. J. Control. Release 271, 98–106. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.12.022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources