The therapeutic efficacy of resveratrol for acute lung injury-A meta-analysis of preclinical trials
- PMID: 36091774
- PMCID: PMC9453560
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.963245
The therapeutic efficacy of resveratrol for acute lung injury-A meta-analysis of preclinical trials
Abstract
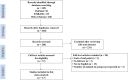
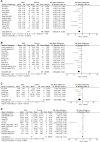
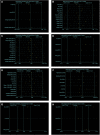
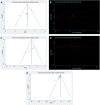
Background: Resveratrol (RES) has a protective effect on acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Our purpose was to conduct a meta-analysis to investigate the efficacy of RES for ALI/ARDS in animal models. Methods: PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science were searched to screen relevant preclinical trials. The standardized mean difference (SMD) was used to compare the lung injury score, lung wet-dry weight ratio (W/D ratio), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, IL-10, the number of neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and the total protein in BALF between the treatment and control groups. SYRCLE's risk of bias tool was used for quality assessment. Results: A total of 17 studies published from 2005 to 2021 were included in our study to calculate the SMD with corresponding confidence interval (CI). As compared with controls, RES significantly decreased the lung injury score (SMD -2.06; 95% CI -2.77, -1.35; p < 0.00001) and W/D ratio (SMD -1.92; 95% CI -2.62, -1.22; p < 0.00001). RES also reduced the number of neutrophils in BALF (SMD -3.03; 95% CI -3.83, -2.24; p < 0.00001) and the total protein in BALF (SMD -5.59; 95% CI -10.10, -1.08; p = 0.02). Furthermore, RES was found to downregulate proinflammatory mediators such as TNF-α (SMD -2.02; 95% CI -3.09, -0.95; p = 0.0002), IL-1β (SMD -2.51; 95% CI -4.00, -1.02; p = 0.001) and IL-6 (SMD -2.26; 95% CI -3.49, -1.04; p = 0.0003). But RES had little effect on the anti-inflammatory mediators such as IL-10 (SMD 2.80; 95% CI -0.04, 5.63; p = 0.05). Sensitivity analysis and stratified analysis were performed for the outcome indicators with heterogeneity. Conclusion: RES treatment is effective on reducing the severity of ALI. However, more animal studies and human trials are needed for further investigation. Our study may provide a reference for preclinical and clinical studies in the future to some extent.
Keywords: acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; animal models; meta−analysis; resveratrol.
Copyright © 2022 Tang, Fu, Wei, Liu, Wu and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of emodin on acute lung injury: a meta-analysis of preclinical trials.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Dec 2;24(1):596. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03406-x. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39623403 Free PMC article.
-
[Aspirin reduces lung inflammatory response in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome: a Meta-analysis based on animal experiments].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Dec;36(12):1261-1267. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231011-00862. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39780669 Chinese.
-
The efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome-a meta-analysis of preclinical trials.Respir Res. 2020 Nov 20;21(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01574-y. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 33218340 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Attenuate Infection-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Animal Experiments: A Meta-Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720969186. doi: 10.1177/0963689720969186. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33164559 Free PMC article.
-
Association between inflammatory biomarkers and acute respiratory distress syndrome or acute lung injury risk : A systematic review and meta-analysis.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2022 Jan;134(1-2):24-38. doi: 10.1007/s00508-021-01971-3. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2022. PMID: 34860273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stand Up to Stand Out: Natural Dietary Polyphenols Curcumin, Resveratrol, and Gossypol as Potential Therapeutic Candidates against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 6;15(18):3885. doi: 10.3390/nu15183885. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Qinhuo Shanggan oral solution resolves acute lung injury by down-regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascade and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 25;14:1285550. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1285550. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37954597 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Pharmacology and Transcriptomics Predicts Resveratrol Will Ameliorate Microplastics-Induced Lung Damage by Targeting Ccl2 and Esr1.Toxics. 2024 Dec 14;12(12):910. doi: 10.3390/toxics12120910. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39771125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alghetaa H., Mohammed A., Sultan M., Busbee P., Murphy A., Chatterjee S., et al. (2018). Resveratrol protects mice against SEB−induced acute lung injury and mortality by miR−193a modulation that targets TGF−beta signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 22 (5), 2644–2655. 10.1111/jcmm.13542 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bo S., Ciccone G., Castiglione A., Gambino R., De Michieli F., Villois P., et al. (2013). Anti−inflammatory and antioxidant effects of resveratrol in healthy smokers a randomized, double−blind, placebo−controlled, cross−over trial. Curr. Med. Chem. 20 (10), 1323–1331. 10.2174/0929867311320100009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

