Metformin suppresses proliferation and differentiation induced by BMP9 via AMPK signaling in human fetal lung fibroblast-1
- PMID: 36091775
- PMCID: PMC9448853
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984730
Metformin suppresses proliferation and differentiation induced by BMP9 via AMPK signaling in human fetal lung fibroblast-1
Abstract
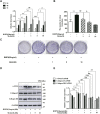
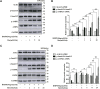
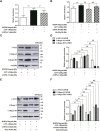
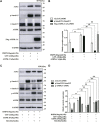
Adenosine monophosphosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its activator metformin were found to be involved in the regulation of fibroblast activation and pulmonary fibrosis. However, the regulatory mechanism has been undetermined. Recently, AMPK has been reported to exert its effect through inhibiting bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathway. In this study, human fetal lung fibroblast (HFL-1) cells were treated with metformin or specific AMPKα1 mutants, including constitutively activated mutant (AMPK-CA) and dominant negative mutant (AMPK-DN), combined with BMP9, and then the absorbance of these cells was measured by cell counting kit (CCK)-8 assay. The colony number of HFL-1 cells stimulated by metformin with or without BMP9 was examined by colony formation assay. The protein expressions of differentiated markers (α-smooth muscle actin, collagen I and collagen III) and the key molecules of BMP9 signaling, including activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) one and phosphorylated small mother against decapentaplegic (p-Smad)1/5, were also evaluated by western blot. Data revealed that BMP9 induced the proliferation and differentiation of HFL-1 cells which was suppressed by metformin or AMPK-CA. Meanwhile, the effect of metformin on BMP9-induced activation was counteracted by AMPK-DN. In addition, we found that the expressions of ALK1 and p-Smad1/5 induced by BMP9 were attenuated by metformin and AMPK-CA, whereas the inhibitory responses of metformin to the increased ALK1 and p-Smad1/5 were reduced by AMPK-DN. Accordingly, these results suggested that metformin mitigated BMP9-induced proliferation and differentiation of HFL-1 cells, which was achieved partly through the activation of AMPK and inhibition of ALK1/Smad1/5 signaling.
Keywords: AMPK; BMP9; differentiation; lung fibroblast; metformin; proliferation.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Wang, Sheng and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exogenous BMP9 promotes lung fibroblast HFL-1 cell activation via ALK1/Smad1/5 signaling in vitro.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):728. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10160. Epub 2021 May 4. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34007337 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin inhibits ALK1-mediated angiogenesis via activation of AMPK.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(20):32794-32806. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15825. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28427181 Free PMC article.
-
BMP9 attenuates occurrence of venous malformation by maintaining endothelial quiescence and strengthening vessel walls via SMAD1/5/ID1/α-SMA pathway.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020 Oct;147:92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.07.010. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32730768
-
New insights into BMP9 signaling in organ fibrosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 5;882:173291. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173291. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32574673 Review.
-
Potential roles of BMP9 in liver fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 11;15(11):20656-67. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120656. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25393508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

