The efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies
- PMID: 36091777
- PMCID: PMC9449963
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.950450
The efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies
Abstract
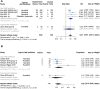
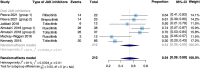
Background: Due to the lack of comprehensive evidence based on prospective studies, the efficacy and safety of Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors (including tofacitinib, ruxolitinib, baricitinib, ritlecitinib and brepocitinib) for alopecia areata (AA) are yet to be proved. Methods: The systematic review and meta-analysis was performed pursuant to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline and registered on PROSPERO (CRD42022303007). Results: Fourteen prospective studies (5 RCTs and 9 non-RCTs), enrolling a total of 1845 patients with AA, were included for quantitative analysis. In RCTs, oral JAK inhibitors resulted in higher good response rate compared with control (RR: 6.86, 95% CI: 2.91-16.16); topical JAK inhibitors did not show any difference compared with control (RR: 1.00, 95% CI: 0.31-3.18). In non-RCTs, the pooled rate of good response to oral, topical and sublingual JAK inhibitors were 63% (95% CI: 44%-80%), 28% (95% CI: 1%-72%) and 11% (95% CI: 1%-29%), respectively. The pooled recurrence rate in patients treated with JAK inhibitors was 54% (95% CI: 39%-69%), mainly due to the withdrawal of JAK inhibitors. In RCTs, no difference was found in the risk of experiencing most kind of adverse events; in non-RCTs, the reported adverse events with high incidence rate were mostly mild and manageable. Conclusion: JAK inhibitors are efficacious and generally well-tolerated in treating AA with oral administration, whereas topical or sublingual administration lacks efficacy. Subgroup analyses indicate that baricitinib, ritlecitinib and brepocitinib seem to have equal efficacy for AA in RCTs; ruxolitinib (vs. tofacitinib) and AA (vs. AT/AU) are associated with better efficacy outcomes in non-RCT. Due to the high recurrence rate after withdrawal of JAK inhibitors, continuous treatment should be considered to maintain efficacy. Systematic Review Registration: PROSPERO: CRD 42022303007.
Keywords: JAK inhibitors; alopecia areata; baricitinib; janus kinase inhibitors; meta-analysis; ruxolitinib; systematic review; tofacitinib.
Copyright © 2022 Yan, Fan, Chen, Xia, Wang, Dong, Wang, Niu, Rao, Chen, Nie and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adverse events in patients treated with Jak-inhibitors for alopecia areata: A systematic review.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 Apr 4. doi: 10.1111/jdv.19090. Online ahead of print. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023. PMID: 37013725 Review.
-
Safety of Janus Kinase inhibitors in Patients with Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review.Clin Drug Investig. 2023 May;43(5):325-334. doi: 10.1007/s40261-023-01260-z. Epub 2023 May 3. Clin Drug Investig. 2023. PMID: 37138134 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment outcome of oral tofacitinib and ruxolitinib in patients with alopecia areata: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021 Sep-Oct;87(5):621-627. doi: 10.25259/IJDVL_975_19. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021. PMID: 34379968
-
Treatments for Moderate-to-Severe Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Narrative Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Dec;13(12):2951-2991. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01044-5. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37833617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors in the treatment of moderate-to-severe alopecia areata: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 10;15:1372810. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1372810. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38659584 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical and Genetic Aspects of Alopecia Areata: A Cutting Edge Review.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;14(7):1362. doi: 10.3390/genes14071362. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient-Reported Burden of Severe Alopecia Areata: First Results from the Multinational Alopecia Areata Unmet Need Survey.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024 Mar 29;17:751-761. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S445646. eCollection 2024. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38566887 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Survival and Long-term Outcome of Tofacitinib in Patients with Alopecia Areata: A Retrospective Study.Acta Derm Venereol. 2023 Nov 13;103:adv13475. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v103.13475. Acta Derm Venereol. 2023. PMID: 37955531 Free PMC article.
-
Survey on Alopecia Areata Patients' Reported Factors that Determine Severity of Alopecia Areata: A Nationwide Multicenter Study.Ann Dermatol. 2024 Dec;36(6):376-383. doi: 10.5021/ad.24.033. Ann Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39623614 Free PMC article.
-
Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Alopecia Areata: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jun 1;6(6):e2320351. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20351. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37368402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akl E. A., Altman D. G., Aluko P., Askie L. M., Young C. (2019). Cochrane Handbook for systematic Reviews of interventions. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

