Effects of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. on hypertension and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36091787
- PMCID: PMC9453491
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.976247
Effects of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. on hypertension and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
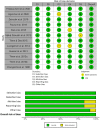
Hypertension and diabetes mellitus are among the most prevalent diseases affecting people from all walks of life. Medicinal herbs have garnered interest as potential agents for the prevention and treatment of diabetes mellitus and hypertension due to their multiple beneficial effects. Piper sarmentosum Roxb. (PS) is an edible medicinal plant that has been traditionally used in Asia for treating hypertension and diabetes mellitus. This review is aimed to provide comprehensive information from the literature on the effects of PS on hypertension and diabetes mellitus. A computerized database search was performed on Scopus, PubMed and Web of Science databases with the following set of keywords: Piper sarmentosum AND diabetes mellitus OR diabetic OR diabetes OR hyperglyc*emia OR blood glucose OR HbA1c OR glycated h*emoglobin OR h*emoglobin A1c OR hyperten* OR blood pressure. A total of 47 articles were screened and 14 articles published between the years 1998 until 2021 were included for data extraction, comprising of six articles on antihypertensive and eight articles on antidiabetic effects of PS. These studies consist of two in vitro studies and eleven in vivo animal studies. Meta-analysis of three studies on hypertension showed that PS versus no treatment significantly lowered the systolic blood pressure with mean difference (MD) -39.84 mmHg (95% confidence interval (CI) -45.05, -34.62; p < 0.01), diastolic blood pressure with MD -26.68 mmHg (95% CI -31.48, -21.88; p < 0.01), and mean arterial pressure with MD -30.56 mmHg (95% CI -34.49, -26.63; p < 0.01). Most of the studies revealed positive effects of PS against hypertension and diabetes mellitus, suggesting the potential of PS as a natural source of antidiabetic and antihypertensive agents.
Keywords: Piper sarmentosum; antidiabetic; antihypertensive; diabetes mellitus; hypertension.
Copyright © 2022 Othman, Che Roos, Aminuddin, Murthy, A. Hamid and Ugusman.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Piper sarmentosum Roxb.: A review on its botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Dec 5;263:112897. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112897. Epub 2020 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32620264 Review.
-
Use Piper sarmentosum as an effective antidiabetic supplement in South East Asia: a review.Clin Ter. 2012 Nov;163(6):505-10. Clin Ter. 2012. PMID: 23306747 Review.
-
Effects of tai chi on physiology, balance and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Rehabil Med. 2019 Jun 18;51(6):405-417. doi: 10.2340/16501977-2555. J Rehabil Med. 2019. PMID: 30968941
-
Effect of Piper chaba Hunter, Piper sarmentosum Roxb. and Piper interruptum Opiz. on natural killer cell activity and lymphocyte proliferation.J Med Assoc Thai. 2014 Aug;97 Suppl 8:S133-9. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014. PMID: 25518305
-
The use of Piper sarmentosum leaves aqueous extract (Kadukmy™) as antihypertensive agent in spontaneous hypertensive rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Mar 10;15:54. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0565-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25887182 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
In silico identification of compounds from Piper sarmentosum Roxb leaf fractionated extract inhibit interleukin-6 to prevent rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1358037. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1358037. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38576490 Free PMC article.
-
Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Inhibits Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Activity in Phorbol 12-Myristate-13-Acetate-Induced Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 28;25(5):2806. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052806. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed O. M., Mahmoud A. M., Abdel-Moneim A., Ashour M. B. (2012). Antidiabetic effects of hesperidin and naringin in type 2 diabetic rats. Diabetol. Croat. 41 (2), 53–67.
-
- Alwi N. A. N. M., Zakaria Z., Karim A. A. H., Nordin N. A. M. M., Ugusman A. (2018). Antihypertensive effect of Piper sarmentosum in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Sains Malays. 47 (10), 2421–2428. 10.17576/jsm-2018-4710-18 - DOI
-
- Amalan V., Vijayakumar N. (2015). Antihyperglycemic effect of P-coumaric acid on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Indian J. Appl. Res. 5 (1), 1–4.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

