Loss of MHC-I antigen presentation correlated with immune checkpoint blockade tolerance in MAPK inhibitor-resistant melanoma
- PMID: 36091815
- PMCID: PMC9459091
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.928226
Loss of MHC-I antigen presentation correlated with immune checkpoint blockade tolerance in MAPK inhibitor-resistant melanoma
Abstract
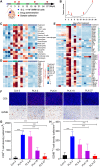
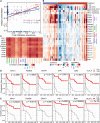
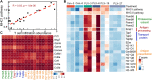
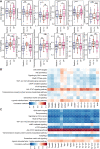
Immune checkpoint blockade and MAPK-targeted combined therapy is a promising regimen for advanced melanoma patients. However, the clinical benefit from this combo regimen remains limited, especially in patients who acquired resistance to MAPK-targeted therapy. Here, we systematically characterized the immune landscape during MAPK-targeted therapy in patients and mouse melanoma models. We observed that both the abundance of tumor-infiltrated T cells and the expression of immune-related genes were upregulated in the drug-responsive period, but downregulated in the resistance period, implying that acquired drug resistance dampens the antitumor immune response. Further transcriptomic dissection indicated that loss of MHC-I antigen presentation on tumor cells plays a critical role in the reduction of T cell infiltration during drug resistance. Survival analysis demonstrates that loss of antigen presentation and reduction of T-cell infiltration during acquired drug resistance are associated with poorer clinical response and prognosis of anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients. In addition, we identified that alterations in the MAPK inhibitor resistance-related oncogenic signaling pathway closely correlated with deficiency of MHC-I antigen presentation, including activation of the PI3K-mTOR, MAPK, and Wnt pathways. In conclusion, our research illuminates that decreased infiltration of T cells is associated with acquired drug resistance during MAPK-targeted therapy, which may underlie the cross-resistance to immune checkpoint blockade.
Keywords: MAPK-targeted therapy; MHC-I antigen presentation; drug resistance (DR); immune checkpoint blockade; melanoma; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Yu, Wu, Song, Zhao, Li, Luo and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeting the MAPK and PI3K pathways in combination with PD1 blockade in melanoma.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Oct 14;5(12):e1238557. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1238557. eCollection 2016. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 28123875 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of MAPK inhibition with photothermal therapy synergistically augments the anti-tumor efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade.J Control Release. 2021 Apr 10;332:194-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.02.020. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 33631225
-
An experimental model of anti-PD-1 resistance exhibits activation of TGFß and Notch pathways and is sensitive to local mRNA immunotherapy.Oncoimmunology. 2021 Mar 16;10(1):1881268. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1881268. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 33796402 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors to Overcome Resistance to Targeted and Immuno Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 17;8:486. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00486. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32626712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of MAPK Pathway Activation in BRAF(V600) Melanoma on T Cell and Dendritic Cell Function.Front Immunol. 2013 Oct 28;4:346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00346. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24194739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of non-classical Wnt signaling pathway effectively enhances HLA-A presentation in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 19;14:1336106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1336106. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38962268 Free PMC article.
-
Current knowledge about immunotherapy resistance for melanoma and potential predictive and prognostic biomarkers.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 May 13;7:17. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.150. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38835341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photothermally sensitive gold nanocage augments the antitumor efficiency of immune checkpoint blockade in immune "cold" tumors.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 24;14:1279221. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279221. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37942337 Free PMC article.
-
Microparticle-Delivered Cxcl9 Prolongs Braf Inhibitor Efficacy in Melanoma.Cancer Immunol Res. 2023 May 3;11(5):558-569. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0224. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 36820825 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Autophagy by Berbamine Hydrochloride Mitigates Tumor Immune Escape by Elevating MHC-I in Melanoma Cells.Cells. 2024 Sep 13;13(18):1537. doi: 10.3390/cells13181537. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329721 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

