Network pharmacology and experimental analysis to reveal the mechanism of Dan-Shen-Yin against endothelial to mesenchymal transition in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 36091823
- PMCID: PMC9449326
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.946193
Network pharmacology and experimental analysis to reveal the mechanism of Dan-Shen-Yin against endothelial to mesenchymal transition in atherosclerosis
Abstract
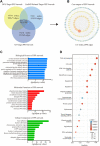
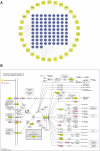
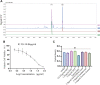
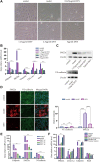
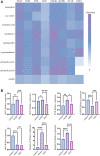
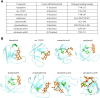
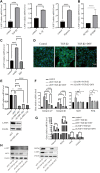
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of plaque and endothelial dysfunction. Under pro-inflammatory conditions, endothelial cells adopt a mesenchymal phenotype by a process called endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) which plays an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Dan-Shen-Yin (DSY) is a well-known traditional Chinese medicine used in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. However, the molecular mechanism whereby DSY mitigates atherosclerosis remains unknown. Therefore, we employed a network pharmacology-based strategy in this study to determine the therapeutic targets of DSY, and in vitro experiments to understand the molecular pharmacology mechanism. The targets of the active ingredients of DSY related to EndMT and atherosclerosis were obtained and used to construct a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network followed by network topology and functional enrichment analysis. Network pharmacology analysis revealed that the PI3K/AKT pathway was the principal signaling pathway of DSY against EndMT in atherosclerosis. Molecular docking simulations indicated strong binding capabilities of DSY's bioactive ingredients toward PI3K/AKT pathway molecules. Experimentally, DSY could efficiently modify expression of signature EndMT genes and decrease expression of PI3K/AKT pathway signals including integrin αV, integrin β1, PI3K, and AKT1 in TGF-β2-treated HUVECs. LASP1, which is upstream of the PI3K/AKT pathway, had strong binding affinity to the majority of DSY's bioactive ingredients, was induced by EndMT-promoting stimuli involving IL-1β, TGF-β2, and hypoxia, and was downregulated by DSY. Knock-down of LASP1 attenuated the expression of integrin αV, integrin β1, PI3K, AKT1 and EndMT-related genes induced by TGF-β2, and minimized the effect of DSY. Thus, our study showed that DSY potentially exerted anti-EndMT activity through the LASP1/PI3K/AKT pathway, providing a possible new therapeutic intervention for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Dan-Shen-Yin; LASP1; PI3K/AKT signaling; atherosclerosis; endothelial to mesenchymal transition; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2022 Hong, Wu, Zhang, Gu, Chen, Guan, Qin, Li and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Constructing a competitive endogenous RNA network of EndMT-related atherosclerosis through weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 10;10:1322252. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1322252. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38268851 Free PMC article.
-
Dan-shen Yin attenuates myocardial fibrosis after myocardial infarction in rats: Molecular mechanism insights by integrated transcriptomics and network pharmacology analysis and experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 10;338(Pt 2):119070. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119070. Epub 2024 Nov 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39522849
-
Dan-Shen-Yin Granules Prevent Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension via STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF and FAK/AKT Signaling Pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 11;13:844400. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.844400. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35479305 Free PMC article.
-
EndMT: Potential Target of H2S against Atherosclerosis.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(18):3666-3680. doi: 10.2174/0929867327999201116194634. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33200693 Review.
-
Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition: An Insight in Atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 17;8:734550. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.734550. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34604359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Constructing a competitive endogenous RNA network of EndMT-related atherosclerosis through weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 10;10:1322252. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1322252. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38268851 Free PMC article.
-
LASP1 in Cellular Signaling and Gene Expression: More than Just a Cytoskeletal Regulator.Cells. 2022 Nov 29;11(23):3817. doi: 10.3390/cells11233817. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the neuroprotective mechanisms of Jiawei Suanzaoren decoction in depression: insights from network pharmacology and molecular docking.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jun 6;25(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04939-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40481474 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-19a-3p inhibits endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis by targeting JCAD.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jul 30;24(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04063-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39080547 Free PMC article.
-
The biomedical knowledge graph of symptom phenotype in coronary artery plaque: machine learning-based analysis of real-world clinical data.BioData Min. 2024 May 21;17(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13040-024-00365-1. BioData Min. 2024. PMID: 38773619 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

